PostgreSQL is an open-source, object-oriented relational database system with reliability, efficiency, and robustness. It helps SQL (relational) and JSON (non-relational) queries.PostgreSQL’s widespread options embrace Multi-Model Concurrency Management (MVCC), point-in-time restoration, granular entry controls, tablespaces, and asynchronous replication.
Knowledge refactoring is a standard requirement in information mining operations. Knowledge saved in a desk requires transformations primarily based on the wants. Let’s say your desk retailer buyer deal with in a column. The deal with accommodates the home quantity, road identify, and postal code. You need to extract a buyer postal code for sorting buyer information as per their location (postal code). Equally, you would possibly want to extract information earlier than or after a specific character, similar to a comma or semi-colon.
PostgreSQL contains a number of built-in capabilities for manipulating string information in fields similar to CONCAT(), FORMAT(), LENGTH (), POSITION(), LTRIM(), RTRIM(), REPLACE(), SUBSTRING().
On this article, we discover how the PostgreSQL substring operate works in extracting particular information from a string,
This text covers the next matters.
-
Substring operate in PostgreSQL -
Examples of Substring capabilities -
Dynamically finding the beginning and finish character positions
Surroundings particulars
This text makes use of PostgreSQL 15.1 on Ubuntu with the pgadmin GUI instrument.
You should use the next hyperlinks to arrange the PostgreSQL surroundings.
PostgreSQL: https://www.postgresql.org/obtain/
PgAdmin: https://www.pgadmin.org/obtain/
PostgreSQL substring operate
The PostgreSQL substring operate returns a subset of the enter string primarily based on the provided string beginning place and size. You should use the SUBSTRING operate for extracting information as per fastened string size and common expressions.
Syntax:
SUBSTRING (String, Start_Position, size)
-
String: The enter string with information sort char, varchar, textual content, datetime, and many others. -
Start_Position: It’s an integer worth (optimistic) that specifies the beginning character place of the string. The primary character within the string has the start_position worth as one. If you don’t specify any start_position worth, PostgreSQL at all times units the beginning place from the primary character. -
Size: Size can be a optimistic integer that defines the variety of characters you should extract from the required string starting on the start_position. It’s an elective parameter. If we don’t specify the size parameter, the PostgreSQL substring operate returns the entire ranging from the start_position.
Let’s discover the substring operate with varied examples.
-
Instance: SUBSTRING() operate with a string
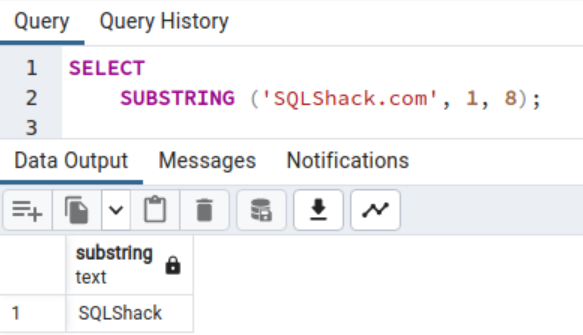
The next substring operate extracts a string of 8th characters from the beginning place 1. The primary character in a string at all times has a beginning place of 1.
|
SELECT SUBSTRING (SQLShack.com, 1, 8);
|

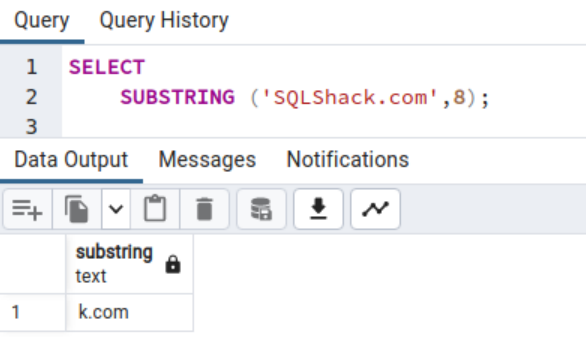
The size parameter is elective within the substring operate. If you don’t specify it, all characters from the beginning place are returned. For instance, within the following code, the output is the string from the 8th place character.

- Instance: SUBSTRING operate with another syntax
Within the earlier instance, we specified string, start_position, and size (elective) parameters separated by commas. Alternatively, you need to use the next format to get the identical output.
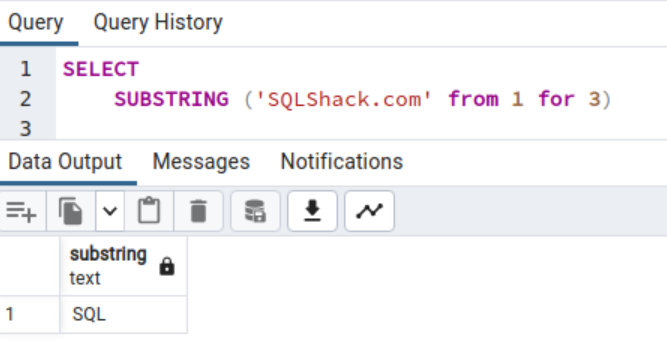
This format specifies the parameters in a human-friendly method. For instance, the next code instructs Postgres to extract the string from the beginning place 1 with three characters in size.
|
SELECT SUBSTRING (‘SQLShack.com’ from 1 for 3)
|

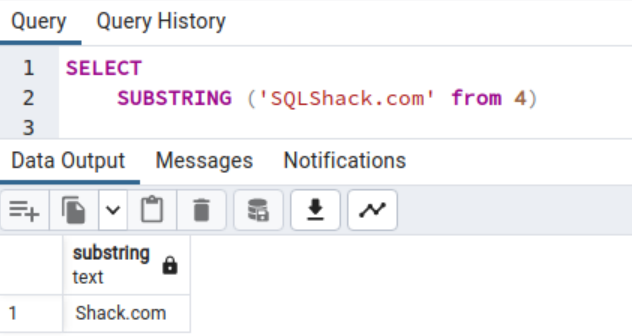
Equally, if you don’t require a size parameter, specify the beginning place per the question under.
|
SELECT SUBSTRING (‘SQLShack.com’ from 4)
|

- Instance: SUBSTRING operate with desk information
We now have a desk within the pattern database named actor that has the next content material:
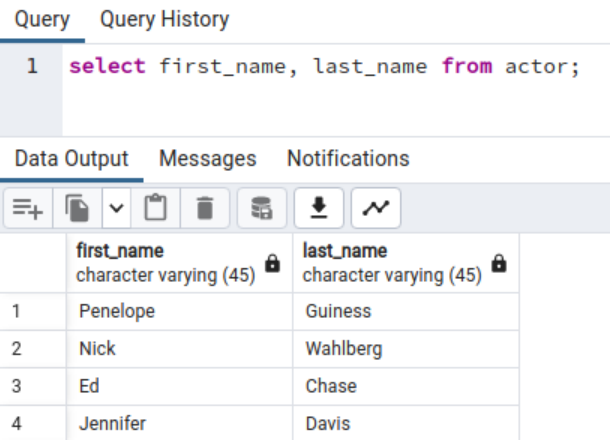

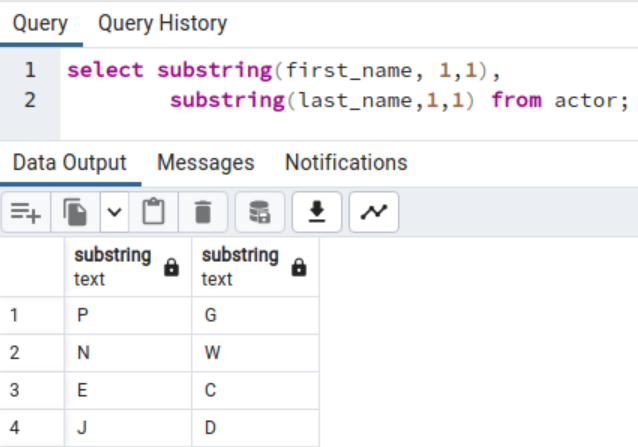
We are able to use the substring operate with the columns to extract a particular string portion. The next question extracts the primary character of the primary and final identify from the actor desk.
|
choose substring(first_name, 1,1), substring(last_name,1,1) from actor;
|

-
Instance: SUBSTRING operate with the ORDER BY clause
This instance makes use of SUBSTRING() operate with the ORDER BY clause for sorting information as per the extracted string.
|
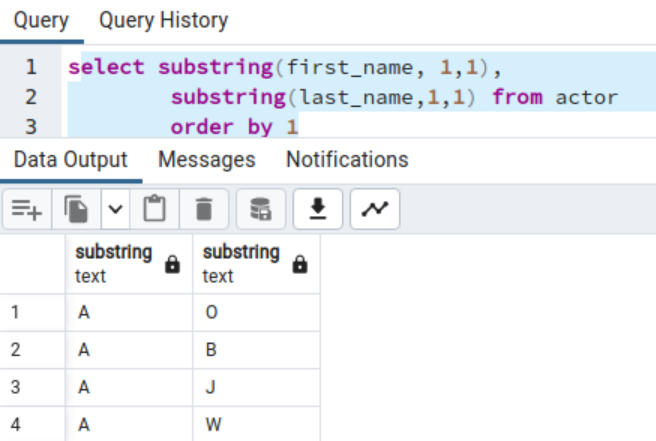
choose substring(first_name, 1,1), substring(last_name,1,1) from actor order by 1
|
Right here, the ORDER BY 1 exhibits information sorting is required as per the content material of the primary column.

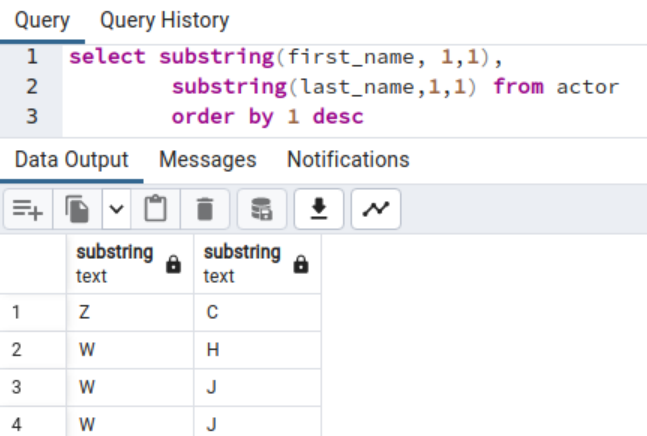
In the event you want information sorted in descending order, add the DESC key phrase with the ORDER BY clause.

Extract matching Substrings with SQL Common Expression
Postgres SUBSTRING operate can extract string that matches with common expressions. Common expressions are the patterns that can be utilized to match character combos in strings. These expressions can use the next operators:
Bracket [ ]: The bracket expression matches the only character from the characters vary specified within the brackets. For instance, [a-z] specifies a spread that matches any lowercase letter from “a” to “z.” Equally, [1-9] specifies the vary matching numbers 1 to 9.
^: It matches the beginning place throughout the string.
$: It matches the ending place of the string or a place simply earlier than a string-ending newline.
[^ ]: It matches a single character not contained throughout the brackets.
Let’s take a look at the next code that makes use of the common expression. On this code, we’ve the followings:
String: That is my 600th article
Common expression: [0-9]
Beginning place: 1
Size: 600
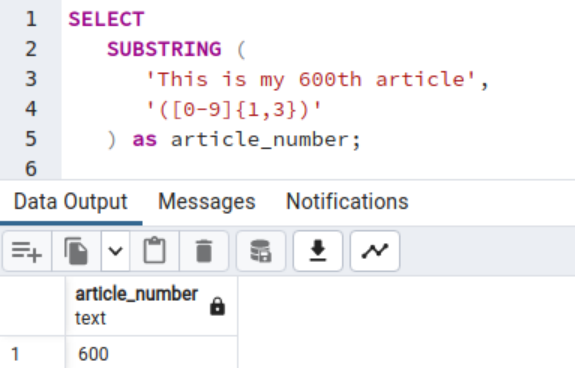
The code interpretation is extracting the substring the place a primary place character is a quantity between 0 to 9. Due to this fact, the code returns the worth 600 specified within the code.
SELECT
|
SELECT SUBSTRING ( ‘That is my 600th article’, ‘([0-9]{1,3})’ ) as article_number;
|

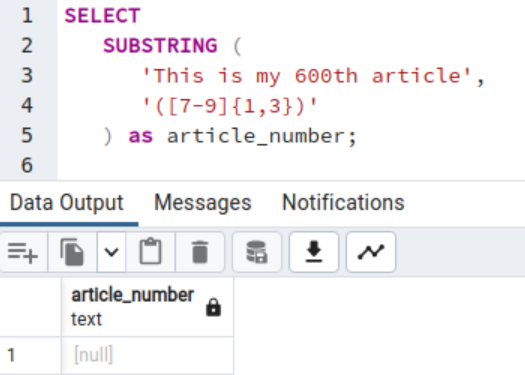
If we alter the common expression to [7-9], we get a NULL worth within the output as a result of the string doesn’t have a personality the place the quantity is between 7 to 9.

-
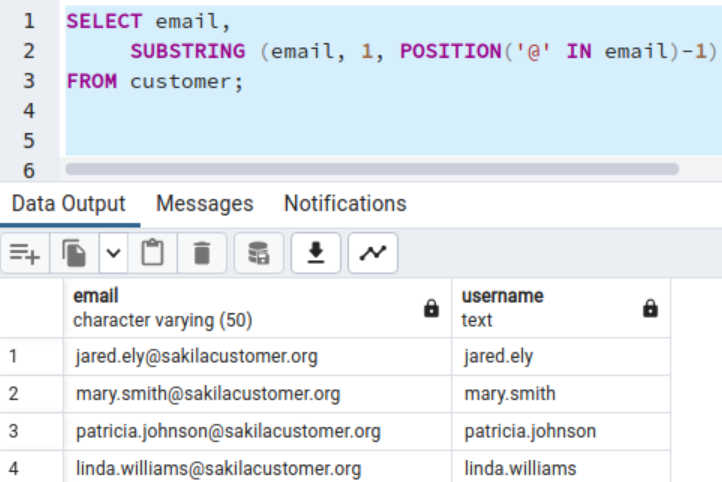
Instance: Work with the e-mail addresses utilizing the SUBSTRING operate
Suppose your organization makes use of the e-mail deal with within the format the place the string earlier than the @ key phrase is the client person identify that the worker makes use of to login to the net portal. How do you extract the person identify from the e-mail deal with on this case?
The POSITION operate returns the numeric character place of the character (@). Right here, we don’t require (@) from the extracted string. Due to this fact, we use the minus 1 within the place operate.
|
SELECT electronic mail, SUBSTRING (electronic mail, 1, POSITION(‘@’ IN electronic mail)–1) AS username FROM buyer;
|
Use a Damaging quantity as beginning place within the SUBSTRING operate
Suppose you specified the unfavorable quantity for the start_position of the SUBSTRING operate. The operate takes the primary character place as 1. Due to this fact, as outlined within the operate -5 worth considers the empty string 5 characters again from the primary character and returns the variety of characters you laid out in size.
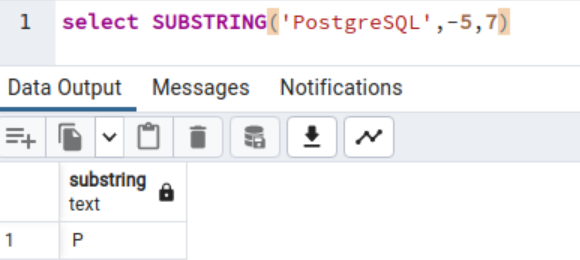

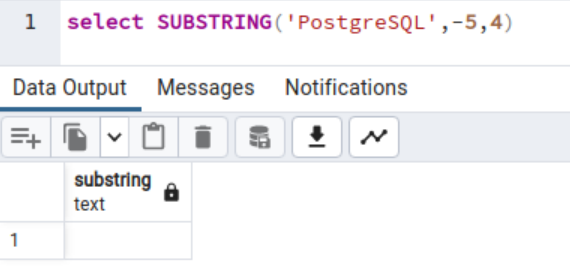
The next code returns an empty string as a result of it calculates from the minus 5 character place and takes size as 4 characters. Since we should not have a string on beginning place -5 and size 4, you get the empty string output as under.

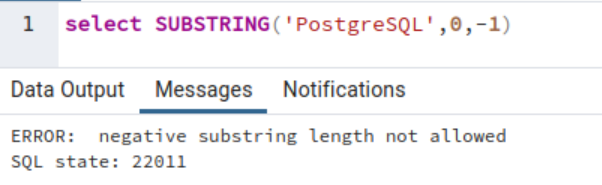
Nevertheless, when you specify the size as a unfavorable worth, you get the error: “unfavorable substring size not allowed, SQL State: 22011”

Conclusion
This text explored the PostgreSQL SUBSTRING() operate that extracts a substring from the required string primarily based on the beginning place and elective size parameter. This operate is often used whenever you work with strings and requires information extraction. Discover this handy operate in your PostgreSQL surroundings.
In conclusion, the substring operate in PostgreSQL is a robust instrument that means that you can extract a portion of a string primarily based on the beginning place and the variety of characters. This operate may be useful in varied situations, similar to extracting elements of names, addresses, or product codes. The substring operate can be case-sensitive, which signifies that it could possibly distinguish between uppercase and lowercase letters. Utilizing the substring operate, you possibly can manipulate and course of string information extra effectively in your database, making it a beneficial instrument for information evaluation and administration.