With MongoDB 8.0, the database engine takes one other step ahead in efficiency optimization, notably in the way it manages reminiscence. Probably the most impactful adjustments beneath the hood is the up to date model of TCMalloc (Thread-Caching Malloc), which impacts how the server allocates, caches, and reuses reminiscence blocks.
For workloads with excessive concurrency, long-running queries, or blended learn/write patterns, the brand new TCMalloc can ship noticeable efficiency positive factors.
This text explains what TCMalloc is, the way it influences efficiency and reminiscence fragmentation, and what variations you’ll be able to count on earlier than and after upgrading to MongoDB 8.0.
What’s TCMalloc?
TCMalloc (Thread-Caching Malloc) is a reminiscence allocator initially developed by Google. It replaces the usual malloc() and free() calls utilized by purposes written in C/C++ with a quicker, multithread-optimized different.
In easy phrases, TCMalloc handles reminiscence requests extra effectively by caching allocations per thread or per-CPU (default), avoiding the competition that may occur when a number of threads attempt to allocate or free reminiscence on the identical time.
TCMalloc could function in one in all two fashions:
- (default) per-CPU caching, the place TCMalloc maintains reminiscence caches native to particular person logical cores.
- per-thread caching, the place TCMalloc maintains reminiscence caches native to every software thread.
In each circumstances, these cache implementations permit TCMalloc to keep away from requiring locks for many reminiscence allocations and deallocations. It ends in low reminiscence fragmentation and diminished system calls that within the majority of circumstances supplies higher efficiency.
TCMalloc in MongoDB 8.0
MongoDB has used TCMalloc as its default allocator, however model 8.0 features a main improve to a more moderen implementation aligned with upstream Google TCMalloc adjustments that makes use of per-CPU caches, as a substitute of per-thread caches.
This brings improved multithreaded scalability, higher reminiscence launch conduct to the OS, extra predictable RSS (Resident Set Dimension) beneath heavy workloads.
The improve notably advantages deployments the place:
- A number of shards or duplicate set members share the identical host (not likely advisable when you don’t use containers).
- Massive in-memory datasets (working units) are incessantly altering, and also you see elevated variety of evictions from the WiredTiger cache.
- Workloads generate many short-lived allocations (e.g., aggregation pipelines, complicated queries, or analytical jobs).
Evidently, due to this beneath the hood change, MongoDB 8.0 is asserted to be quicker than earlier model 7.0 for lots of use circumstances.
The official documentation says that MongoDB 8.0 introduces important efficiency enhancements from MongoDB 7.0, together with, however not restricted to:
- As much as 36% higher learn throughput.
- As much as 32% higher efficiency for typical internet purposes.
- As much as 20% quicker concurrent writes throughout replication.
In all probability the advance isn’t solely from TCMalloc, nevertheless it might be the primary contributor.
Essential change for Clear Big Pages (THP)
If you’re a very long time person of MongoDB, you in all probability know that one of many extra frequent greatest practices for OS tuning was to disable THP. Ranging from MongoDB 8.0 the most effective follow is precisely the other: with the intention to profit from the brand new TCMalloc, THP now have to be enabled.
The next circumstances have to be checked to make sure TCMalloc can actually use the brand new per-CPU caches:
- Kernel model 4.18 or later
- THP enabled
- glibc rseq disabled: if one other software, such because the glibc library, registers an rseq construction earlier than TCMalloc, TCMalloc can’t use rseq. With out rseq, TCMalloc makes use of per-thread caches, that are utilized by the legacy TCMalloc model.
A number of particulars about Rseq (Restartable Sequences). Rseq lets user-space code execute small vital sections which can be assured to run atomically on the identical CPU, with out utilizing locks or syscalls within the quick path. Some operations are extraordinarily frequent and performance-critical, like: updating per-CPU counters, accessing per-CPU knowledge constructions, quick reminiscence allocators and schedulers. As a way to advantage of it, TCMalooc have to be the one to register an rseq construction.
To confirm that TCMalloc is working with per-CPU caches, guarantee the next from the serverStatus:
- tcmalloc.usingPerCpuCaches is true
- tcmalloc.tcmalloc.cpu_free is bigger than 0
Have a look at the next web page for extra particulars:
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/v8.0/administration/tcmalloc-performance/
Testing time
Let’s now do some assessments working the identical form of workloads and examine MongoDB 7.0 vs MongoDB 8.0.
The servers used for the assessments had the next specs:
- 4 CPU
- 4 GB RAM
- OS Ubuntu 24.04 LTS
POCDriver was used to generate the workloads. Each take a look at ran for 10 minutes on each servers utilizing 4 parallel threads.
The 2 variations in contrast had been Percona Server for MongoDB 7.0.26-14 and Percona Server for MongoDB 8.0.16-5.
Listed below are the outcomes of the assessments. Increased is healthier.
INTENSIVE INSERTS AND UPDATES WITH OTHER READS
avg ops per sec
| PSMDB 7.0 | PSMDB 8.0 | % enchancment | |
| INSERTS | 55,784 | 71,752 | +28.62% |
| _id LOOKUPS | 1.883 | 2,529 | +34.31% |
| UPDATES | 17,178 | 17,963 | +4.57% |
| RANGE QUERIES | 753 | 874 | +16.07% |
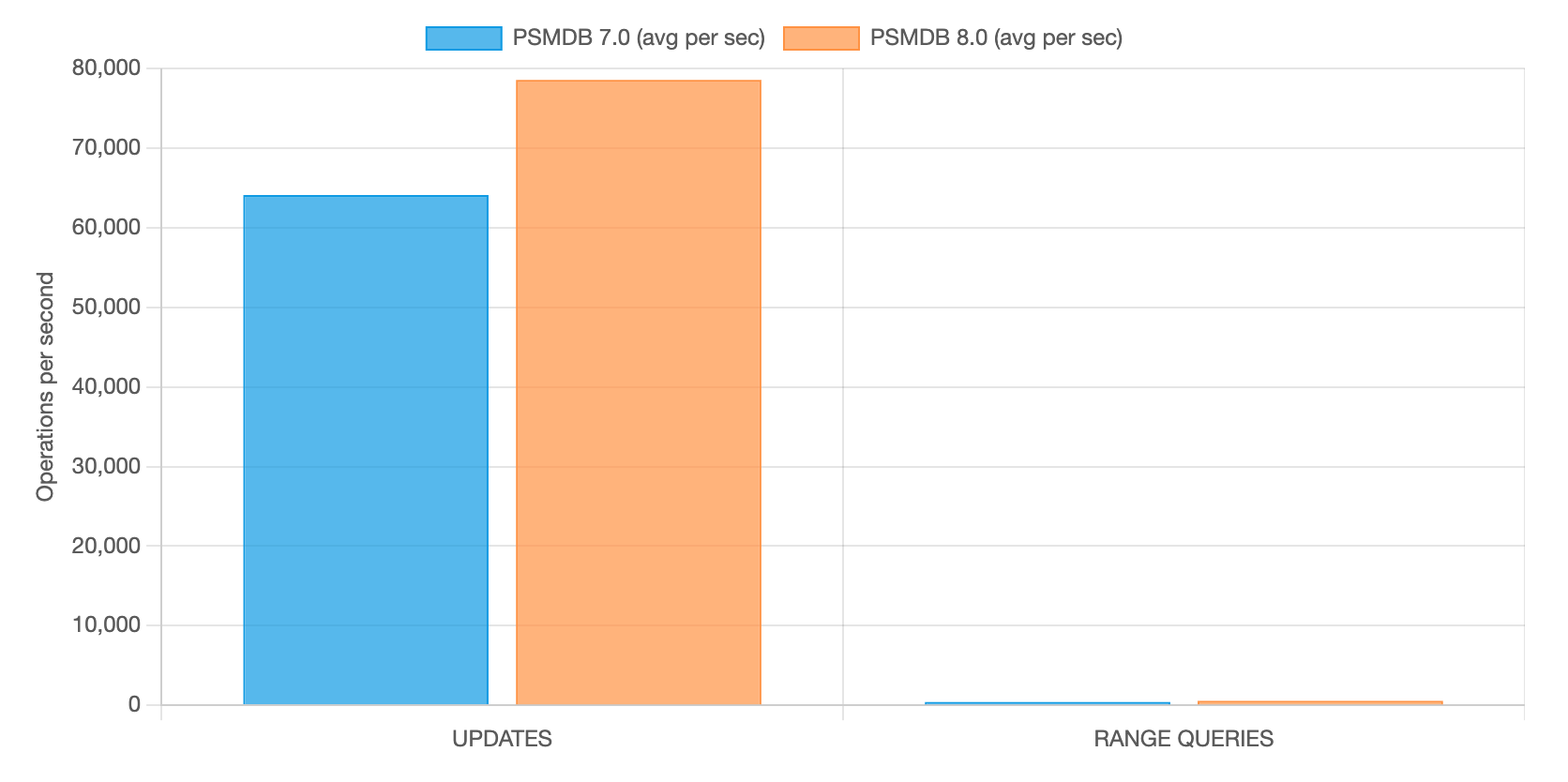
INTENSIVE UPDATES AND RANGE QUERIES
avg ops per sec
| PSMDB 7.0 | PSMDB 8.0 | % enchancment | |
| INSERTS | 0 | 0 | – |
| _id LOOKUPS | 0 | 0 | – |
| UPDATES | 64,091 | 78,568 | +22.59% |
| RANGE QUERIES | 411 | 565 | +37.47% |
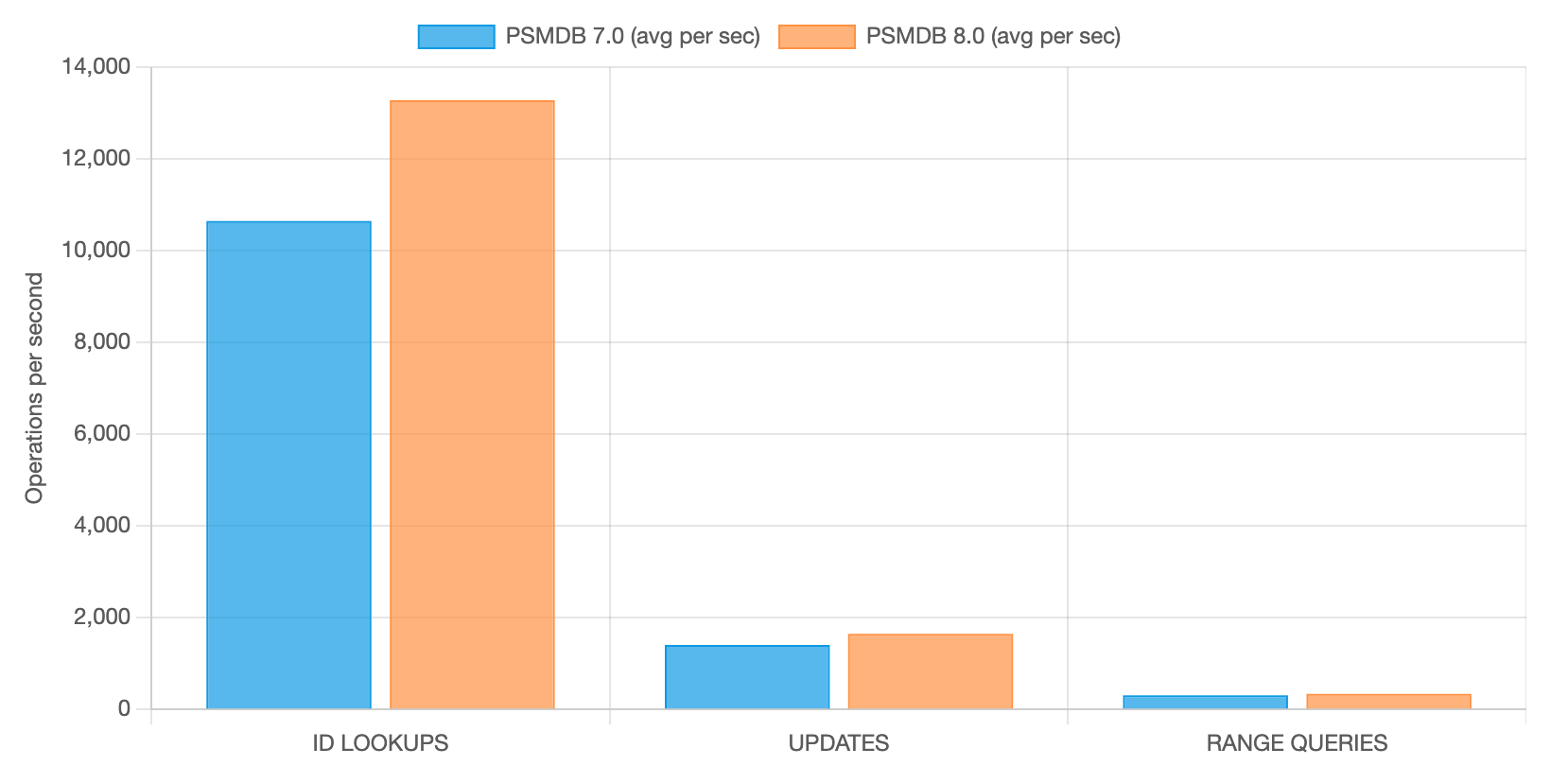
INTENSIVE _id LOOKUPS WITH FEW UPDATES AND RANGE QUERIES
avg ops per sec
| PSMDB 7.0 | PSMDB 8.0 | % enchancment | |
| INSERTS | 0 | 0 | – |
| _id LOOKUPS | 10.647 | 13,279 | +24.72% |
| UPDATES | 1,408 | 1,647 | +16.97% |
| RANGE QUERIES | 307 | 339 | +10.42% |
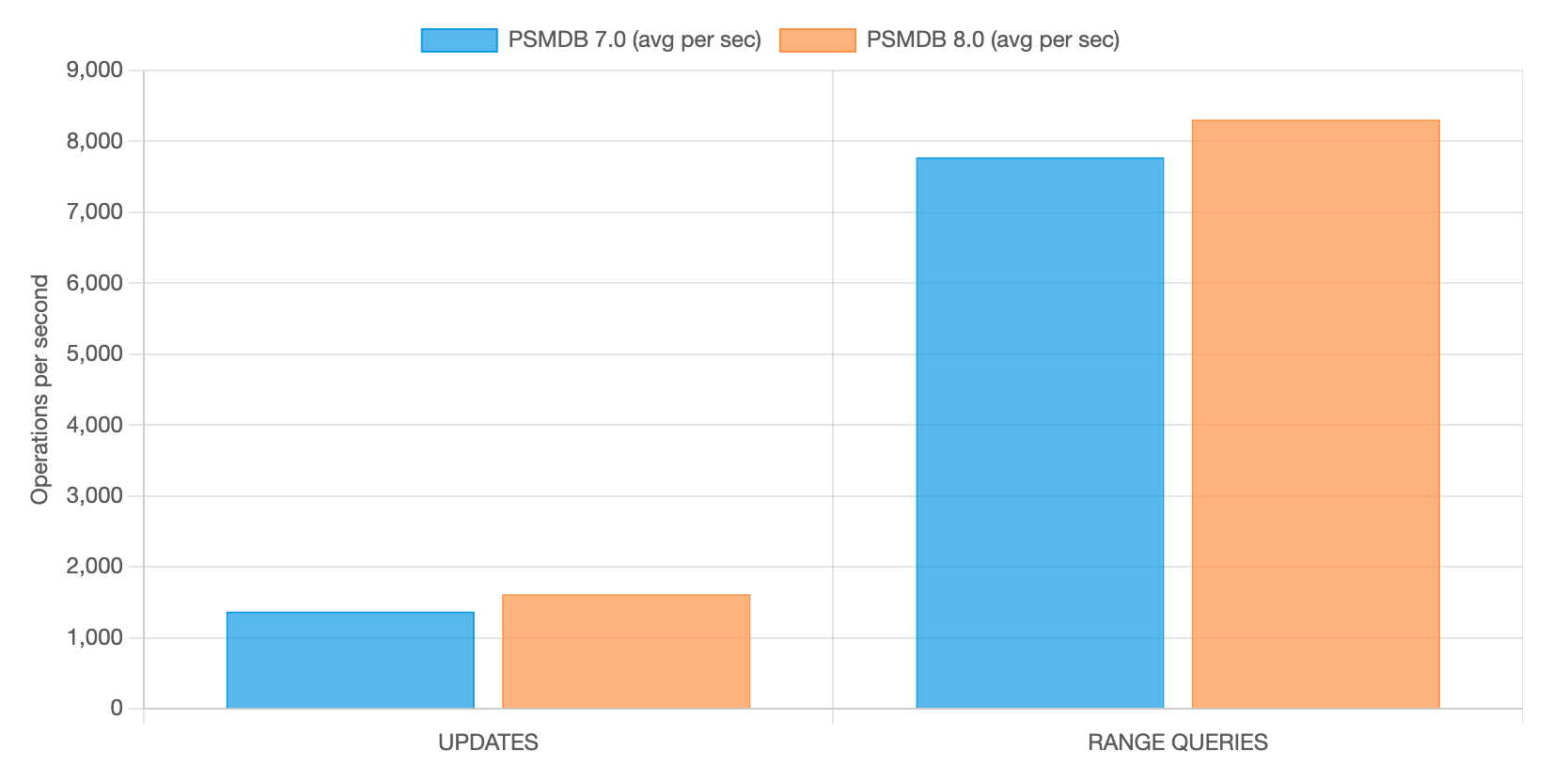
INTENSIVE RANGE QUERIES AND UPDATES
avg ops per sec
| PSMDB 7.0 | PSMDB 8.0 | % enchancment | |
| INSERTS | 0 | 0 | – |
| _id LOOKUPS | 0 | 0 | – |
| UPDATES | 1,372 | 1,615 | +17.71% |
| RANGE QUERIES | 7,779 | 8,307 | +6.79% |
Conclusions
As promised by the official documentation, MongoDB 8.0 is de facto quicker than MongoDB 7.0. The assessments offered outcomes that verify the advantages declared. Clearly, the actual advantages rely on a number of elements, like a custom-made tuning, a distinct {hardware} or different issues. You might face a particular state of affairs that can’t present the identical form of enhancements we had. For that reason, working assessments towards a brand new model is at all times advisable earlier than transferring a model to manufacturing. Anyway, we’re assured the advantages offered by the brand new TCMalloc with per-CPU caches are actually spectacular.