LLMs aren’t restricted to AI and associated fields! They’re powering virtually each tech, and thereby is among the most requested about matters in interviews. This makes it important to have a floor degree familiarity of the know-how.
This text is designed to reflect how LLMs present up in actual interviews. We’ll begin from first ideas and construct ahead, so even if you happen to’re new to the subject, you’ll be capable to comply with the logic behind every reply as an alternative of memorizing jargon.
We’ll begin by offering 10 interview questions that problem the fundamentals of LLMs. Then we’d transfer on to extra nuanced questions.
Frequent LLM Interview Questions
Essentially the most ceaselessly requested questions on LLMs requested in an interview.
Q1. What’s a Massive Language Mannequin (LLM)?
A. An LLM is a machine studying mannequin educated on huge textual content to generate and interpret human language.
What which means is
- It learns patterns from large textual content information
- It predicts the following token based mostly on context
- Language understanding emerges from scale, not guidelines
Be aware: The interviewers need readability, not a textbook definition. In case you gained’t add your personal expertise of utilizing LLMs on this response, it’d sound robotic.
Q2. How do LLMs generate textual content?
A. LLMs behave like extremely superior programs for predicting the following token in a sequence. At every step, the mannequin calculates possibilities over all attainable subsequent tokens based mostly on the context thus far.
By repeating this course of many instances, longer and seemingly coherent responses emerge, despite the fact that the mannequin is simply making native, step-by-step predictions.
What occurs throughout era
- Enter is transformed into tokens
- The mannequin assigns possibilities to attainable subsequent tokens
- One token is chosen and appended
- The method repeats
Be aware: There’s no understanding, solely statistical continuation. Because of this fashions are sometimes described as impassive. They generate phrases with out intent, so the responses can really feel mechanical.
Q3. What downside did transformers remedy in comparison with older NLP fashions?
A. Earlier NLP fashions struggled to retain which means throughout lengthy sequences of textual content. Transformers allowed for utilization of consideration mechanisms, which targeted on particular elements of the textual content — over everything of it — based mostly on its weightage within the context of the general textual content.
What transformers modified:
- Consideration changed recurrence
- Tokens can “take a look at” all different tokens straight
- Coaching grew to become parallelizable
This resulted in higher context dealing with + large scalability.
This autumn. How are LLMs educated?
A. LLMs be taught by predicting the following phrase repeatedly throughout large quantities of textual content.
It consists of three levels:
- Pretraining on giant, common textual content corpora
- Positive-tuning for particular duties or directions
- Alignment utilizing human suggestions (usually RLHF)
The coaching is completed in a probabilistic method. That means the efficiency positive aspects are measures when it comes to loss%.
Q5. What function does consideration play in LLMs?
A. Consideration permits the mannequin to focus selectively on probably the most related elements of enter.
Why it issues:
- Not all phrases contribute equally
- Consideration assigns dynamic significance
- Permits long-context reasoning
As each “so, like..” may not be contributing to the general textual content. With out consideration, efficiency collapses on complicated language duties.
Q6. What are the primary limitations of LLMs?
A. Regardless of their capabilities, LLMs endure from hallucinations, bias, and excessive operational prices.
- Hallucinations from guessing probably solutions
- Bias from the lopsided information the mannequin was educated on
- Excessive compute and vitality prices from giant mannequin measurement
LLMs optimize for probability, not fact. As talked about beforehand, fashions lack an understanding of knowledge. So the mannequin generates textual content based mostly on which phrases are most definitely, even when they’re incorrect.
Q7. What are widespread real-world functions of LLMs?
A. LLMs are used wherever language-heavy work might be automated or assisted. Newer fashions are able to aiding in non-language work information as properly.
- Query answering
- Summarization
- Content material era
- Code help
Ensure that to incorporate the widespread functions solely. Extracting textual content, creating ghibli photos and so forth. aren’t widespread sufficient and might be labeled in one of many earlier classes.
Good sign so as to add: Tie examples to the corporate’s area.
Q8. What’s fine-tuning, and why is it wanted?
A. Positive-tuning adjusts a general-purpose LLM to behave higher for particular duties. It’s like having a bit of clothes intently fitted to a selected measurement.
Why it issues:
- Base fashions are broad
- Companies want specificity
- Positive-tuning aligns conduct with intent
Why is it wanted? As a result of most use circumstances are particular. A fin-tech may not require the coding-expertise options that comes together with a mannequin. Finetuning assures {that a} mannequin that was generic initially, will get tailor-made to a selected use case.
Q9. What moral dangers are related to LLMs?
A. LLMs introduce moral challenges that scale as shortly as their adoption. Among the dangers are:
- Bias amplification
- Private identification info leakage
- Misuse at scale
Ethics transcend philosophy. When folks deploy LLMs at scale, errors could cause catastrophic disruption. Subsequently, it’s important to have guardrails in place to mitigate that from occurring. AI governance is the way in which to go.
Q10. How do you consider the standard of an LLM?
A. Analysis begins with measurable system-level efficiency indicators. The expansion (or discount in some circumstances) determines how properly the mannequin is performing. Folks consider LLMs utilizing metrics like:
To judge an LLM’s high quality qualitatively, folks use the next metrics:
- Factuality
- Coherence
- Usefulness
Mix computerized metrics with human analysis.
Past the Fundamentals LLM Questions
At this level, you must have a transparent psychological mannequin of what an LLM is, the way it works, and why it behaves the way in which it does. That’s the inspiration most candidates cease at.
However interviews don’t.
When you’ve proven you perceive the mechanics, interviewers begin probing one thing deeper: how these fashions behave in actual programs. They need to know whether or not you possibly can cause about reliability, limitations, trade-offs, and failure modes.
The following set of questions are right here to help with that!
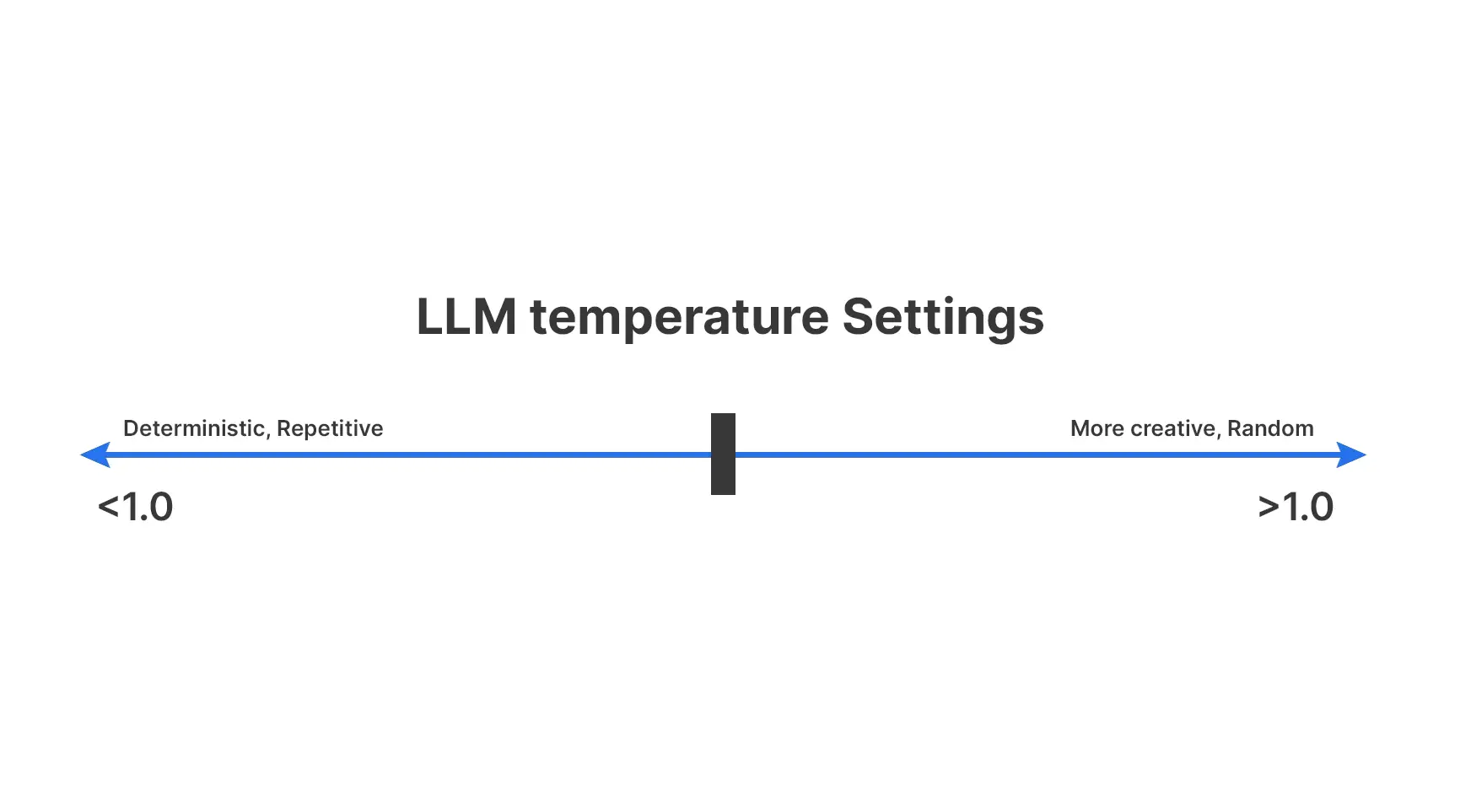
Q11. What’s the function of temperature in textual content era?
A. Temperature controls how a lot randomness an LLM permits when selecting the following token. This straight influences whether or not outputs keep conservative and predictable or change into numerous and inventive.
For temperature the rule of thumb is as follows:
- Low temperature favors safer, widespread tokens
- Greater temperature will increase variation
- Very excessive values can harm coherence
Temperature tunes model, not correctness. It determines how a lot emphasis must be given in direction of an issue.
Q12. What’s top-p (nucleus) sampling, and why is it used?
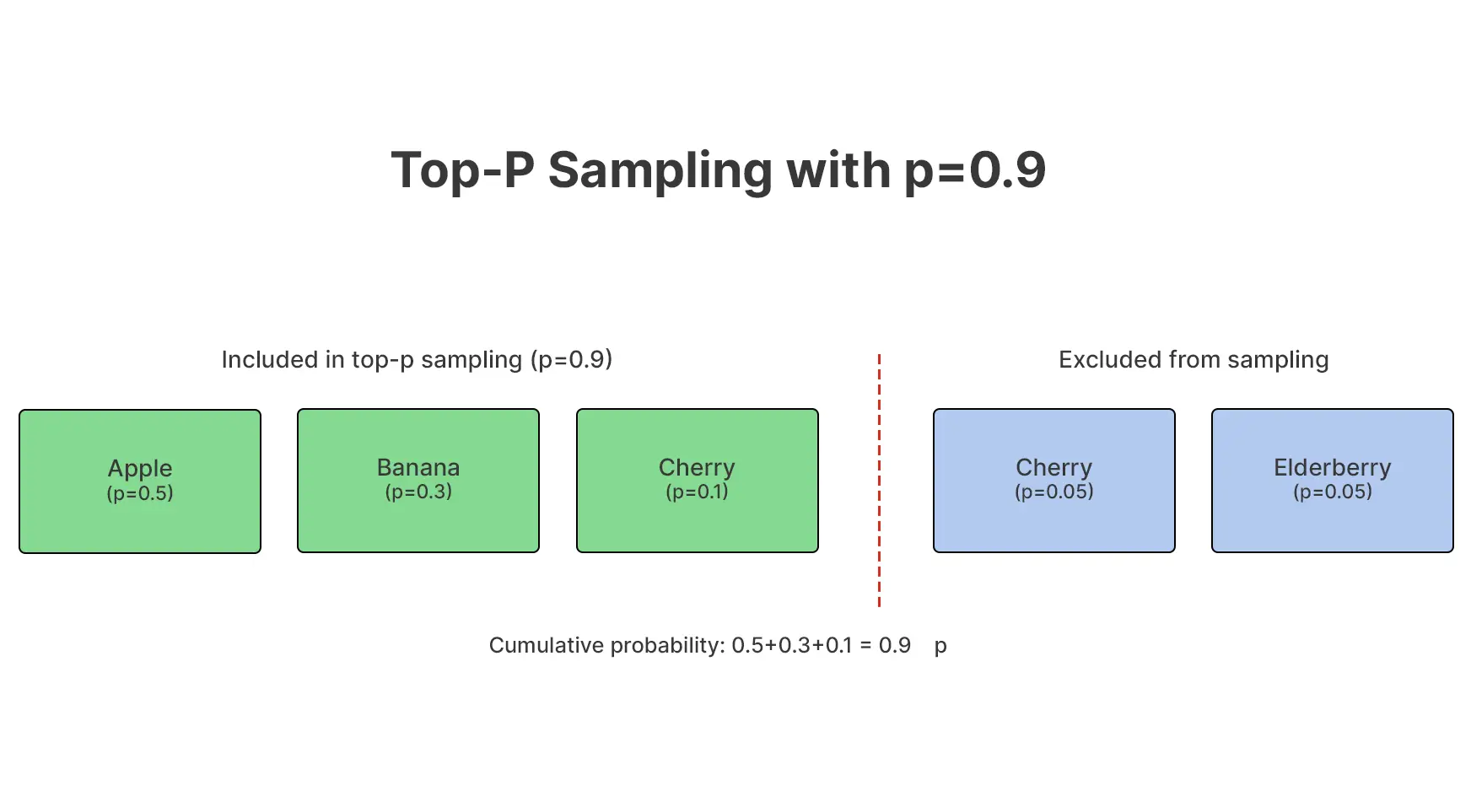
A. Prime-p sampling limits token choice to the smallest set whose cumulative likelihood exceeds a threshold, permitting the mannequin to adaptively steadiness coherence and variety as an alternative of counting on a hard and fast cutoff.
Why groups want it
- Adjusts dynamically to confidence
- Avoids low-quality tail tokens
- Produces extra pure variation
It controls which choices are thought-about, not what number of.
Q13. What are embeddings, and why are they necessary?
A. Embeddings convert textual content into dense numerical vectors that seize semantic which means, permitting programs to check, search, and retrieve info based mostly on which means fairly than precise wording.
What embeddings allow
- Semantic search
- Clustering comparable paperwork
- Retrieval-augmented era
They let machines work with which means mathematically.
Q14. What’s a vector database, and the way does it work with LLMs?
A. A vector database shops embeddings and helps quick similarity search, making it attainable to retrieve probably the most related context and feed it to an LLM throughout inference.
Why this issues
- Conventional databases match key phrases
- Vector databases match intent
- Retrieval reduces hallucinations
This turns LLMs from guessers into grounded responders.
Q15. What’s immediate injection, and why is it harmful?
A. Immediate injection happens when consumer enter manipulates the mannequin into ignoring unique directions, doubtlessly resulting in unsafe outputs, information leakage, or unintended actions.
Typical dangers
- Overriding system prompts
- Leaking inner directions
- Triggering unauthorized conduct
LLMs comply with patterns, not authority. It’s like altering the hardwired protocols that had been set in stone for an LLM.
Q16. Why are LLM outputs non-deterministic?
A. LLM outputs range as a result of era depends on probabilistic sampling fairly than fastened guidelines, which means the identical enter can produce a number of legitimate responses.
Key contributors
- Temperature
- Sampling technique
- Random seeds
It’s not a particular set of steps which can be adopted that results in a conclusion. On the flipside, its a path to a vacation spot, which may range.
Fast comparability
| Idea | What it controls | Why it issues |
| Temperature | Randomness of token selection | Impacts creativity vs stability |
| Prime-p | Token choice pool | Prevents low-quality outputs |
| Embeddings | Semantic illustration | Permits meaning-based retrieval |
| Vector DB | Context retrieval | Grounds responses in information |
Q17. What’s quantization in LLM deployment?
A. Quantization reduces mannequin measurement and inference value by reducing numerical precision of weights, buying and selling small accuracy losses for important effectivity positive aspects.
Why groups use it
- Sooner inference
- Decrease reminiscence utilization
- Cheaper deployment
It optimizes feasibility, not intelligence.
Q18. What’s Retrieval-Augmented Era (RAG)?
A. RAG is a way the place an LLM pulls info from an exterior data supply earlier than producing a solution, as an alternative of relying solely on what it realized throughout coaching.
What truly occurs
- The system converts the consumer question into an embedding.
- The system retrieves related paperwork from the vector database.
- The system injects that context into the immediate.
- The LLM solutions utilizing each the immediate and retrieved information
Why it issues
As soon as LLMs are educated, they will’t be up to date. RAG provides them entry to reside, personal, or domain-specific data with out retraining the mannequin. That is how chatbots reply questions on firm insurance policies, product catalogs, or inner paperwork with out hallucinating.
Q19. What’s mannequin fine-tuning vs immediate engineering?
A. Each goal to form mannequin conduct, however they work at completely different ranges.
| Facet | Immediate Engineering | Positive-tuning |
| What it adjustments | What you ask the mannequin | How the mannequin behaves internally |
| When it occurs | At runtime | Throughout coaching |
| Value | Low-cost | Dearer |
| Velocity to use | Quick | Gradual |
| Stability | Breaks simply when prompts get complicated | Far more steady |
| Finest used when | You want fast management over one process | You want constant conduct throughout many duties |
What this actually means: If you need the mannequin to comply with guidelines, model, or tone extra reliably, you fine-tune. If you wish to information one particular response, you immediate. Most actual programs use each.
Q20. Why do LLMs typically hallucinate?
A. Hallucinations occur as a result of LLMs goal to provide the most definitely continuation of textual content, not probably the most correct one.
Why it happens
- The mannequin doesn’t verify information
- It fills gaps when data is lacking
- It’s rewarded for sounding assured and fluent
If the mannequin doesn’t know the reply, it nonetheless has to say one thing. So it guesses in a means that appears believable. That’s the reason programs that use retrieval, citations, or exterior instruments are rather more dependable than standalone chatbots.
Conclusion
Massive language fashions can really feel intimidating at first, however most interviews don’t check depth. They check readability. Understanding the fundamentals, how LLMs work, the place folks use them, and the place they fall brief usually provides you adequate to reply thoughtfully and confidently. With these widespread questions, the aim isn’t to sound technical. It’s to sound knowledgeable.
Login to proceed studying and revel in expert-curated content material.

