Compatibility degree in SQL Server refers to a database property that determines the syntax and conduct of the database, permitting it to be appropriate with earlier variations of SQL Server. Every model of SQL Server introduces new options, enhancements, and modifications to the question optimizer, which can have an effect on how queries are executed and the way outcomes are returned.
Setting the compatibility degree of a database means that you can management the model of the SQL Server database, which in flip impacts how the database behaves. That is helpful for sustaining backward compatibility with older purposes or upgrading a SQL Server occasion whereas preserving the conduct of present databases.
On this article, we are going to discover numerous strategies to vary compatibility ranges in SQL Server.
Checklist of compatibility ranges in SQL Server and options launched in every compatibility degree.
This listing particulars SQL Server variations and their native compatibility ranges and supported compatibility ranges:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Microsoft periodically introduces new options and parameters that assist enhance the SQL Server’s efficiency, and deprecates previous syntax and options.
Beneath are new options and configuration parameters launched with new compatibility ranges.
Database compatibility degree 120
- Question Retailer: Question Retailer is a efficiency monitoring and troubleshooting characteristic that means that you can seize and analyze question efficiency knowledge. It helps establish and resolve efficiency points by offering historic details about question execution plans. It means that you can examine efficiency over time and make data-driven selections to optimize question efficiency.
- Stay Question Statistics: Stay Question Statistics is a real-time efficiency monitoring characteristic that means that you can view the progress and particulars of question execution whereas operating. It offers insights into the precise execution plan, the progress of every operation, and the variety of rows processed. It means that you can establish efficiency bottlenecks and optimize queries in actual time.
- Question Retailer Question Efficiency Insights: Question Retailer Question Efficiency Insights is a characteristic that gives graphical representations of question efficiency knowledge collected by Question Retailer. It means that you can simply establish and analyze efficiency points, resembling regressed or improved queries, prime resource-consuming queries, and question execution statistics. It lets you optimize question efficiency.
- Accelerated Database Restoration: Accelerated Database Restoration is a characteristic that improves database restoration efficiency and reduces downtime. It introduces a brand new restoration course of that makes use of a extra environment friendly and optimized algorithm to roll again transactions throughout database restoration. It reduces the restoration occasions and improves database availability.
- Temporal Tables: Temporal Tables, as talked about earlier than, is a characteristic that means that you can observe modifications to knowledge over time. Whereas it offers historic knowledge monitoring capabilities, it will possibly even have efficiency advantages in sure situations. It avoids the necessity for triggers or customized change monitoring mechanisms and permits optimized question efficiency for historic knowledge retrieval.
- Columnstore Index Enhancements: SQL Server 2016 launched a number of enhancements to columnstore indexes, together with assist for updateable non-clustered columnstore indexes, batch mode processing for operational analytics, and improved efficiency for queries involving columnstore indexes. These enhancements can enhance the efficiency of information warehousing and analytics workloads by optimizing the storage and retrieval of huge datasets.
Database compatibility degree 130
The next options and parameters have been launched in compatibility degree 130.
- Batch Mode Adaptive Reminiscence Grant Suggestions: The Batch Mode Adaptive Reminiscence Grant Suggestions characteristic that helps to optimize reminiscence grant allocations for batch mode queries. It permits SQL Server to regulate the reminiscence grants dynamically for batch mode queries primarily based on precise runtime efficiency. It improves the general question efficiency by effectively allocating reminiscence sources.
- Batch Mode on Rowstore: Batch Mode on Rowstore is a characteristic that extends batch mode processing to rowstore indexes. It improves the efficiency of analytical and knowledge warehousing workloads. Additionally, it permits batch mode operations, resembling vectorized question processing, for use with rowstore indexes, leading to sooner question execution for big datasets.
- Approximate Question Processing: Approximate Question Processing is a characteristic that means that you can estimate question outcomes utilizing statistical algorithms as an alternative of executing the entire question. It may be used to rapidly estimate question outcomes for big datasets, bettering question efficiency for advanced analytical queries with aggregations with out processing all the dataset.
- Clever Question Processing: Clever Question Processing is a set of options that makes use of machine studying and question optimization strategies to enhance question efficiency. Some options of Clever Question Processing embrace Batch Mode Adaptive Joins, Desk Variable Deferred Compilation, and Reminiscence-Optimized TempDB Metadata.
- Scalar UDF Inlining: Scalar UDF Inlining is a characteristic that permits scalar user-defined capabilities (UDFs) to be mechanically inlined inside queries. It eliminates the overhead of perform calls and improves question efficiency. This characteristic can considerably velocity up queries that contain scalar UDFs, by avoiding the necessity for separate perform calls and enabling higher question optimization.
Database compatibility degree 150
The next options and parameters have been launched in compatibility degree 150.
- Clever Question Processing: Clever Question Processing is a set of options to enhance question efficiency by optimizing question plans and execution. It consists of options resembling Batch Mode Adaptive Joins, Batch Mode Reminiscence Grant Suggestions, Desk Variable Deferred Compilation, and Scalar UDF Inlining. These options might help enhance question efficiency in numerous situations, resembling large-scale knowledge warehousing and OLTP workloads.
- Accelerated Database Restoration: Accelerated Database Restoration, launched in SQL Server 2019, continues to be a performance-enhancing characteristic. It offers sooner and extra environment friendly restoration of databases after failures or crashes, decreasing downtime and bettering database availability.
- Reminiscence-Optimized TempDB Metadata: In SQL 2019, the metadata of memory-optimized TempDB objects, resembling desk varieties and desk variables, are saved in reminiscence fairly than on disk, which may enhance efficiency for workloads that closely make the most of memory-optimized TempDB objects.
- Resumable On-line Index Rebuilds: SQL Server 2019 launched the power to renew on-line index rebuild operations after interruptions, resembling a database or server restart. This might help scale back downtime and enhance efficiency for index upkeep operations on massive tables.
Necessary Notes
-
While you create a brand new database, the default compatibility degree of the database would be the identical compatibility degree of the mannequin database. For instance, in case you are creating a brand new database in SQL Server 2017, the database’s compatibility degree can be 150. You possibly can change it as per the applying requirement. -
After we restore a database whose backup is taken within the older model to the brand new SQL Server model, the compatibility degree of the restored database will stay unchanged. For instance, suppose you might be restoring a database backup whose compatibility degree is 110 on SQL Server 2017. In that case, the compatibility degree of the database will stay 110. There may be an exception. Suppose the compatibility degree of supply backup is decrease than the minimal compatibility degree supported by SQL Server model. In that case, SQL Server will change the compatibility degree to the bottom supported model. For instance, suppose we restore the backup of the database created in SQL Server 2005 on SQL Server 2017. In that case, the compatibility of the restored database can be modified to 100. -
After we improve the SQL Server model to a more recent model, the compatibility degree of the system database (msdb, mannequin, tempdb and useful resource) can be up to date apart from the grasp database. The compatibility degree of the grasp database will stay unchanged.
View compatibility of SQL Database.
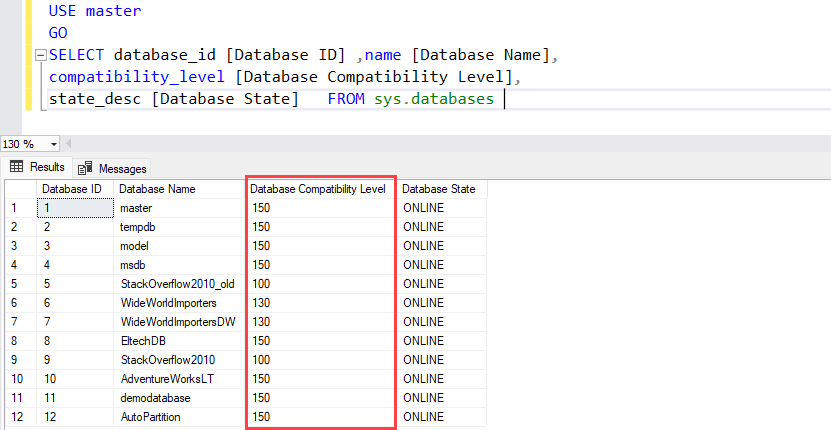
We are able to use sys.databases dynamic administration view to examine the compatibility degree of any SQL database. The column named compatibility_level reveals the present compatibility degree of the database. The question is the next:
|
USE grasp GO SELECT database_id [Database ID] ,identify [Database Name], compatibility_level [Database Compatibility Level], state_desc [Database State] FROM sys.databases
|
Question Output
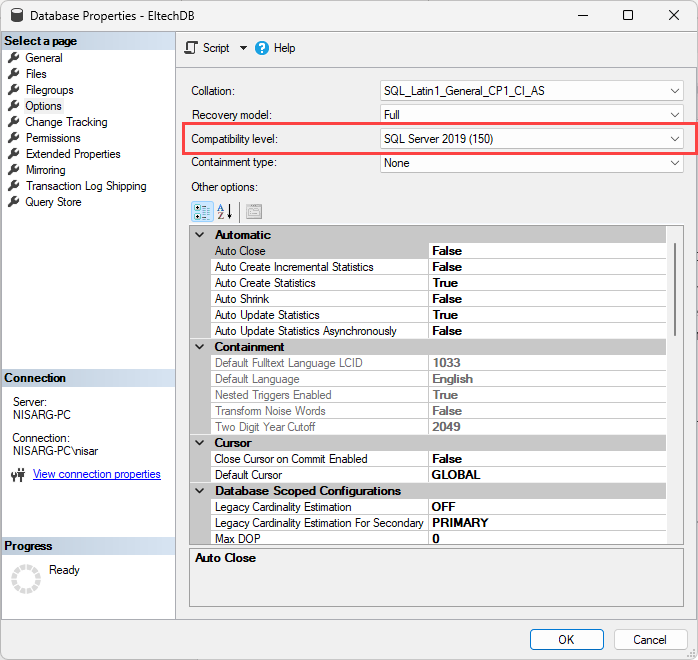
Alternatively, you possibly can view the compatibility degree utilizing SQL Server administration studio. Launch SQL Server Administration Studio 🡪 Connect with SQL server occasion. 🡪 Proper-click on Database and choose Properties. In Database Properties 🡪 choose the Choices web page. You possibly can view the database compatibility in the appropriate pan of the database properties dialog field.
Now, allow us to perceive how we are able to change the compatibility degree of the SQL database.
Change compatibility degree utilizing ALTER DATABASE assertion.
We are able to use ALTER DATABASE assertion to vary the compatibility degree. The syntax is as follows:
|
ALTER DATABASE [db_name] SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL= [compatibility_level];
|
Within the syntax:
- db_name: Specifies the identify of the SQL database whose compatibility degree you wish to change.
- compatibility_level: Specifies the compatibility degree.
Suppose you wish to change the compatibility degree of the demodatabase. The present compatibility degree of the demodatabase is 120, and we’ve upgraded the SQL Server software program however didn’t change the compatibility degree of the database. Now, we wish to change it to 150. The command is the next
|
ALTER DATABASE [demodatabase] SET COMPATIBILITY_LEVEL= 150;
|
Run the next SQL question to confirm the modifications.
|
USE grasp go SELECT identify, compatibility_level FROM sys.databases WHERE identify=‘demodatabase’
|
As you possibly can see, the compatibility degree has been upgraded.
Change compatibility degree utilizing SQL Server Administration Studio
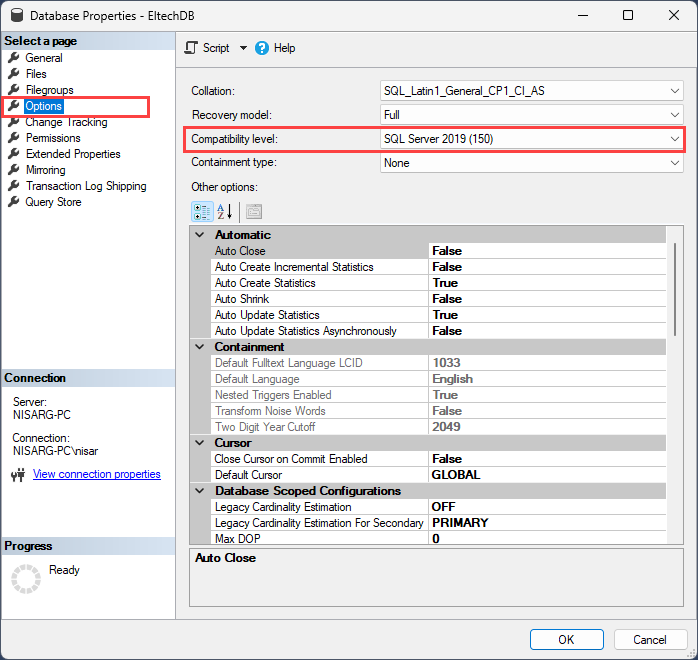
Launch SQL Server Administration Studio 🡪 Connect with SQL server occasion. 🡪 Proper-click on Database and choose Properties. In Database Properties 🡪 choose the Choices web page. You possibly can view the present database compatibility in the appropriate pan of the database properties dialog field. In our demo, the present compatibility of EltechDB database is 120. Choose 150 from the drop-down field and click on OK to use the modifications.
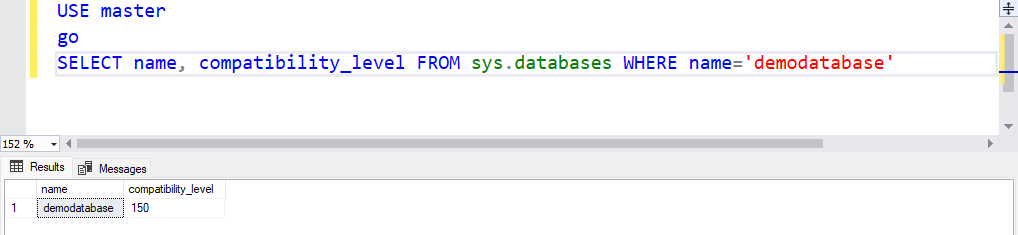
As soon as the compatibility is modified, run the next SQL Question to confirm whether or not modifications have been utilized.
|
USE grasp go SELECT identify, compatibility_level FROM sys.databases WHERE identify=‘eltechdb’
|
As you possibly can see within the above picture, the compatibility of the EltechDB has been modified.
Abstract
On this article, we realized in regards to the strategies of figuring out and altering the compatibility degree in SQL Server. Furthermore, we’ve reviewed the options and enhancements made to every compatibility degree.