The ReWiND technique, which consists of three phases: studying a reward perform, pre-training, and utilizing the reward perform and pre-trained coverage to study a brand new language-specified process on-line.
Of their paper ReWiND: Language-Guided Rewards Educate Robotic Insurance policies with out New Demonstrations, which was offered at CoRL 2025, Jiahui Zhang, Yusen Luo, Abrar Anwar, Sumedh A. Sontakke, Joseph J. Lim, Jesse Thomason, Erdem Bıyık and Jesse Zhang introduce a framework for studying robotic manipulation duties solely from language directions with out per-task demonstrations. We requested Jiahui Zhang and Jesse Zhang to inform us extra.
What’s the matter of the analysis in your paper, and what drawback have been you aiming to unravel?
Our analysis addresses the issue of enabling robotic manipulation insurance policies to unravel novel, language-conditioned duties with out accumulating new demonstrations for every process. We start with a small set of demonstrations within the deployment surroundings, prepare a language-conditioned reward mannequin on them, after which use that discovered reward perform to fine-tune the coverage on unseen duties, with no extra demonstrations required.
Inform us about ReWiND – what are the primary options and contributions of this framework?
ReWiND is a straightforward and efficient three-stage framework designed to adapt robotic insurance policies to new, language-conditioned duties with out accumulating new demonstrations. Its essential options and contributions are:
- Reward perform studying within the deployment surroundings
We first study a reward perform utilizing solely 5 demonstrations per process from the deployment surroundings.- The reward mannequin takes a sequence of photos and a language instruction, and predicts per-frame progress from 0 to 1, giving us a dense reward sign as a substitute of sparse success/failure.
- To reveal the mannequin to each profitable and failed behaviors with out having to gather failed conduct demonstrations, we introduce a video rewind augmentation: For a video segmentation V(1:t), we select an intermediate level t1. We reverse the section V(t1:t) to create V(t:t1) and append it again to the unique sequence. This generates an artificial sequence that resembles “making progress then undoing progress,” successfully simulating failed makes an attempt.
- This enables the reward mannequin to study a smoother and extra correct dense reward sign, bettering generalization and stability throughout coverage studying.
- Coverage pre-training with offline RL
As soon as we’ve the discovered reward perform, we use it to relabel the small demonstration dataset with dense progress rewards. We then prepare a coverage offline utilizing these relabeled trajectories. - Coverage fine-tuning within the deployment surroundings
Lastly, we adapt the pre-trained coverage to new, unseen duties within the deployment surroundings. We freeze the reward perform and use it because the suggestions for on-line reinforcement studying. After every episode, the newly collected trajectory is relabeled with dense rewards from the reward mannequin and added to the replay buffer. This iterative loop permits the coverage to repeatedly enhance and adapt to new duties with out requiring any extra demonstrations.
May you discuss in regards to the experiments you carried out to check the framework?
We consider ReWiND in each the MetaWorld simulation surroundings and the Koch real-world setup. Our evaluation focuses on two features: the generalization capability of the reward mannequin and the effectiveness of coverage studying. We additionally examine how nicely totally different insurance policies adapt to new duties beneath our framework, demonstrating vital enhancements over state-of-the-art strategies.
(Q1) Reward generalization – MetaWorld evaluation
We accumulate a metaworld dataset in 20 coaching duties, every process embrace 5 demos, and 17 associated however unseen duties for analysis. We prepare the reward perform with the metaworld dataset and a subset of the OpenX dataset.
We examine ReWiND to LIV[1], LIV-FT, RoboCLIP[2], VLC[3], and GVL[4]. For generalization to unseen duties, we use video–language confusion matrices. We feed the reward mannequin video sequences paired with totally different language directions and anticipate the accurately matched video–instruction pairs to obtain the best predicted rewards. Within the confusion matrix, this corresponds to the diagonal entries having the strongest (darkest) values, indicating that the reward perform reliably identifies the right process description even for unseen duties.
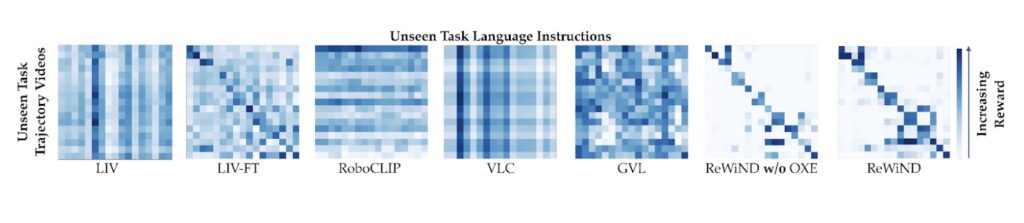 Video-language reward confusion matrix. See the paper for extra data.
Video-language reward confusion matrix. See the paper for extra data.
For demo alignment, we measure the correlation between the reward mannequin’s predicted progress and the precise time steps in profitable trajectories utilizing Pearson r and Spearman ρ. For coverage rollout rating, we consider whether or not the reward perform accurately ranks failed, near-success, and profitable rollouts. Throughout these metrics, ReWiND considerably outperforms all baselines—for instance, it achieves 30% greater Pearson correlation and 27% greater Spearman correlation than VLC on demo alignment, and delivers about 74% relative enchancment in reward separation between success classes in contrast with the strongest baseline LIV-FT.
(Q2) Coverage studying in simulation (MetaWorld)
We pre-train on the identical 20 duties after which consider RL on 8 unseen MetaWorld duties for 100k surroundings steps.
Utilizing ReWiND rewards, the coverage achieves an interquartile imply (IQM) success fee of roughly 79%, representing a ~97.5% enchancment over the most effective baseline. It additionally demonstrates considerably higher pattern effectivity, attaining greater success charges a lot earlier in coaching.
(Q3) Coverage studying in actual robotic (Koch bimanual arms)
Setup: a real-world tabletop bimanual Koch v1.1 system with 5 duties, together with in-distribution, visually cluttered, and spatial-language generalization duties.
We use 5 demos for the reward mannequin and 10 demos for the coverage on this more difficult setting. With about 1 hour of real-world RL (~50k env steps), ReWiND improves common success from 12% → 68% (≈5× enchancment), whereas VLC solely goes from 8% → 10%.
Are you planning future work to additional enhance the ReWiND framework?
Sure, we plan to increase ReWiND to bigger fashions and additional enhance the accuracy and generalization of the reward perform throughout a broader vary of duties. In truth, we have already got a workshop paper extending ReWiND to larger-scale fashions.
As well as, we intention to make the reward mannequin able to straight predicting success or failure, with out counting on the surroundings’s success sign throughout coverage fine-tuning. At the moment, despite the fact that ReWiND supplies dense rewards, we nonetheless depend on the surroundings to point whether or not an episode has been profitable. Our aim is to develop a totally generalizable reward mannequin that may present each correct dense rewards and dependable success detection by itself.
References
[1] Yecheng Jason Ma et al. “Liv: Language-image representations and rewards for robotic management.” Worldwide Convention on Machine Studying. PMLR, 2023.
[2] Sumedh Sontakke et al. “Roboclip: One demonstration is sufficient to study robotic insurance policies.” Advances in Neural Info Processing Programs 36 (2023): 55681-55693.
[3] Minttu Alakuijala et al. “Video-language critic: Transferable reward capabilities for language-conditioned robotics.” arXiv:2405.19988 (2024).
[4] Yecheng Jason Ma et al. “Imaginative and prescient language fashions are in-context worth learners.” The Thirteenth Worldwide Convention on Studying Representations. 2024.
In regards to the authors

|
Jiahui Zhang is a Ph.D. scholar in Pc Science on the College of Texas at Dallas, suggested by Prof. Yu Xiang. He obtained his M.S. diploma from the College of Southern California, the place he labored with Prof. Joseph Lim and Prof. Erdem Bıyık. |

|
Jesse Zhang is a postdoctoral researcher on the College of Washington, suggested by Prof. Dieter Fox and Prof. Abhishek Gupta. He accomplished his Ph.D. on the College of Southern California, suggested by Prof. Jesse Thomason and Prof. Erdem Bıyık at USC, and Prof. Joseph J. Lim at KAIST. |
Lucy Smith
is Senior Managing Editor for Robohub and AIhub.

Lucy Smith
is Senior Managing Editor for Robohub and AIhub.

