In machine studying with categorical knowledge, it’s common to encode the classes as dummy variables (typically known as one sizzling encoding) to encode classes as numerical values. This can be a important step since there are numerous algorithms that don’t function on different issues apart from numbers like linear regression. Nonetheless, there is likely one of the errors that rookies are more likely to make. It’s known as the dummy variable lure. This downside is best understood on the outset to keep away from the confounding of mannequin outcomes and different unwarranted flaws.
What Are Dummy Variables and Why are They Vital?
Most machine studying algorithms are solely in a position to settle for numerical enter. This poses an issue in case our knowledge is about pink, blue, and inexperienced or some other class. Dummy variable helps to resolve this challenge by remodeling categorical knowledge into numbers.
A binary variable is a dummy variable and takes 0 or 1. Using a dummy variable corresponds to a single class and whether or not the class is current or not as regards to a specific knowledge level.
As a living proof, think about a dataset that has a nominal issue often called Colour, which may assume three values, i.e., Purple, Inexperienced, and Blue. To remodel this function into numbers we assemble three new columns:
- Color_Red
- Color_Green
- Color_Blue
The worth of every of those columns might be 1 in a single row and 0 within the remaining rows.
- Assuming a Purple knowledge level, then Colour Purple is 1 and the remainder of the 2 columns are 0.
- In case of the shade Inexperienced, then the shade of Inexperienced is 1 and the remainder are 0.
- When it’s Blue, then Colour-Blue = 1 and Colour-Different = 0.
It’s because, the method permits fashions to study categorical knowledge with out deceptive info. For instance, coding Purple = 1, Inexperienced = 2 and Blue = 3 would falsely point out that Blue is greater than Inexperienced and Inexperienced is greater than Purple. Most fashions would think about these numbers to have an order to them which isn’t what we need.
Succinctly, dummy variables are a secure and clear technique of incorporating categorical variables into machine studying fashions that want numerical knowledge.
What Is the Dummy Variable Lure?
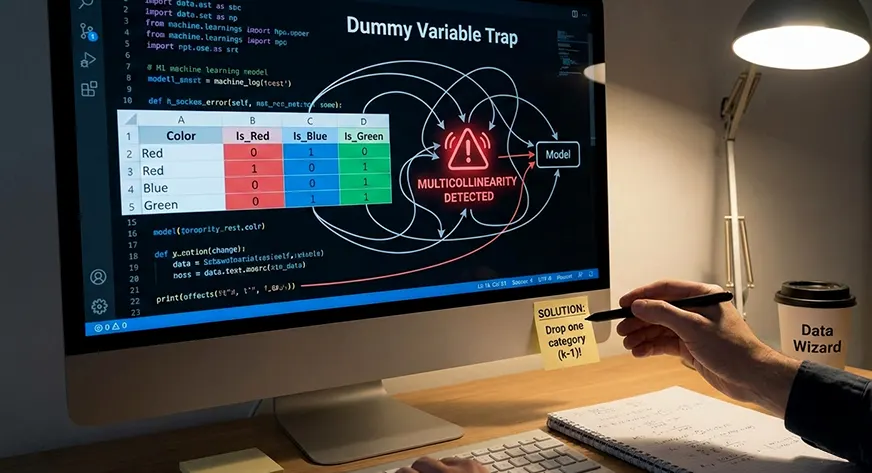
One of the widespread points that arises whereas encoding categorical variables is the dummy variable lure. This downside happens when all classes of a single function are transformed into dummy variables and an intercept time period is included within the mannequin. Whereas this encoding could look right at first look, it introduces good multicollinearity, which means that a number of the variables carry redundant info.
In sensible phrases, the dummy variable lure occurs when one dummy variable will be fully predicted utilizing the others. Since every commentary belongs to precisely one class, the dummy variables for that function at all times sum to at least one. This creates a linear dependency between the columns, violating the belief that predictors ought to be impartial.
Dummy Variable Lure Defined with a Categorical Function
To know this extra clearly, think about a categorical function comparable to Marital Standing with three classes: Single, Married, and Divorced. If we create one dummy variable for every class, each row within the dataset will comprise precisely one worth of 1 and two values of 0. This results in the connection:
Single + Married + Divorced = 1
Since this relationship is unconditionally true, one of many columns is redundant. When one is neither a Single nor Married, then he should be Divorced. The opposite columns may give the identical conclusion. The error is the dummy variable lure. Using dummy variables to signify every class, and a continuing time period, creates good multicollinearity.
On this case, there are potentialities of a number of the dummy variables being completely correlated with others. An instance of that is two dummy columns which transfer in a set other way with one 1 when the opposite is 0. This means that they’re carrying duplicating info. Due to this, the mannequin can’t confirm a definite influence of each variable.
Mathematically, it occurs that the function matrix isn’t full rank, that’s, they’re singular. When that happens then the linear regression can’t calculate a novel mannequin coefficient resolution.
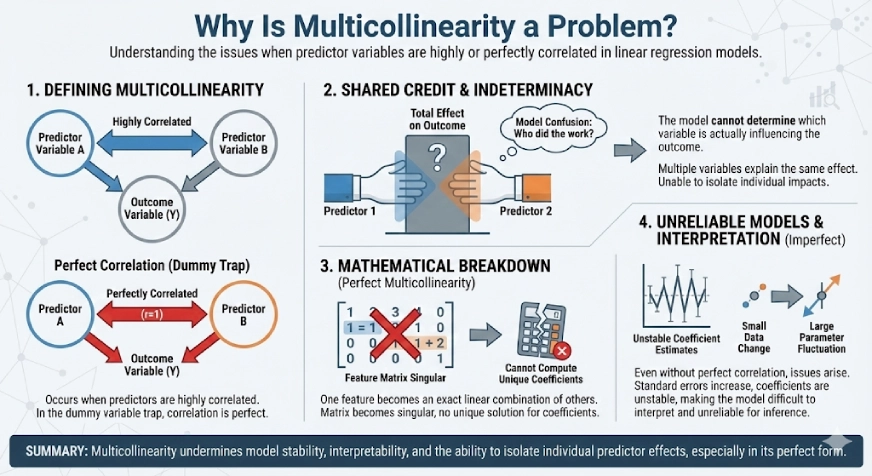
Why Is Multicollinearity a Downside?
Multicollinearity happens when two or extra predictor variables are extremely correlated with one another. Within the case of the dummy variable lure, this correlation is good, which makes it particularly problematic for linear regression fashions.
When predictors are completely correlated, the mannequin can’t decide which variable is definitely influencing the result. A number of variables find yourself explaining the identical impact, much like giving credit score for a similar work to a couple of particular person. Because of this, the mannequin loses the power to isolate the person influence of every predictor.
In conditions of good multicollinearity, the arithmetic behind linear regression breaks down. One function turns into a precise linear mixture of others, making the function matrix singular. Due to this, the mannequin can’t compute a novel set of coefficients, and there’s no single “right” resolution.
Even when multicollinearity isn’t good, it could actually nonetheless trigger critical points. Coefficient estimates turn out to be unstable, customary errors improve, and small adjustments within the knowledge can result in massive fluctuations within the mannequin parameters. This makes the mannequin troublesome to interpret and unreliable for inference.
Instance: Dummy Variable Lure in Motion
To place this level in context, allow us to think about a primary instance.
Allow us to think about a small set of ice cream gross sales. One of many categorical options is Taste, and the opposite numeric goal is Gross sales. The info set consists of three flavors, specifically Chocolate, Vanilla and Strawberry.
We begin with the creation of a pandas DataFrame.
import pandas as pd
# Pattern dataset
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Taste': ['Chocolate', 'Chocolate', 'Vanilla', 'Vanilla', 'Strawberry', 'Strawberry'],
'Gross sales': [15, 15, 12, 12, 10, 10]
})
print(df Output:
This produces a easy desk. Every taste seems twice. Every has the identical gross sales worth.
We then change the Taste column into dummy variables. To illustrate the issue of dummy variables, we’ll artificially generate a dummy column in every class.
# Create dummy variables for all classes
dummies_all = pd.get_dummies(df['Flavor'], drop_first=False)
print(dummies_all) Output:
This leads to three new columns.
- Chocolate
- Vanilla
- Strawberry
The variety of 0s and 1s is proscribed to every column.
A column comparable to Chocolate could be 1 within the occasion of Chocolate taste. The others are 0. The identical argument goes by way of on the opposite flavors.
Now observe one thing of significance. The dummy values in every row are at all times equal to 1.
FlavorChocolate + FlavorVanilla + FlavorStrawberry = 1
This means that there’s an pointless column. Assuming that there are two columns with 0, the third one should be 1. That extra column doesn’t present any new info to the mannequin.
It’s the dummy variable lure. If we add all of the three dummy variables and neglecting so as to add an intercept time period to a regression equation, we obtain good multicollinearity. The mannequin is unable to estimate distinctive coefficients.
The next part will present easy methods to stop this challenge in the fitting means.
Avoiding the Dummy Variable Lure
The dummy variable lure is straightforward to keep away from when you perceive why it happens. The important thing concept is to take away redundancy created by encoding all classes of a function. By utilizing one fewer dummy variable than the variety of classes, you remove good multicollinearity whereas preserving all the knowledge wanted by the mannequin. The next steps present easy methods to appropriately encode categorical variables and safely interpret them in a linear regression setting.
Use ok -1 Dummy Variables (Select a Baseline Class)
The decision to the dummy variable lure is straightforward. One much less dummy variable than the classes.
If a categorical function has ok completely different values, then kind solely ok -1 dummy columns. The class that you simply omit seems to be the class of reference, which can also be the baseline.
There’s nothing misplaced by dropping one of many dummy columns. When the values of all dummies are 0 of a row, the present commentary falls underneath the class of the baseline.
There are three ice cream flavors in our case. That’s to say that we’re to have two dummy variables. We’ll remove one of many flavours and make it our baseline.
Stopping the Dummy Variable Lure Utilizing pandas
By conference, one class is dropped throughout encoding. In pandas, that is simply dealt with utilizing drop_first=True.
# Create dummy variables whereas dropping one class
df_encoded = pd.get_dummies(df, columns=['Flavor'], drop_first=True)
print(df_encoded)Output:
The encoded dataset now seems to be like this:
- Gross sales
- Flavor_Strawberry
- Flavor_Vanilla
Chocolate doesn’t have its column. Chocolate has turn out to be the reference level.
The rows are all simple to know. When the Strawberry is 0 and Vanilla is 0, then the taste ought to be Chocolate. The redundancy is now non-existent. The impartial variables are the dummy ones.
Then, it’s how we escape the lure of the dummy variable.
Decoding the Encoded Knowledge in a Linear Mannequin
Now let’s match a easy linear regression mannequin. We’ll predict Gross sales utilizing the dummy variables.
This instance focuses solely on the dummy variables for readability.
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
# Options and goal
X = df_encoded[['Flavor_Strawberry', 'Flavor_Vanilla']]
y = df_encoded['Sales']
# Match the mannequin
mannequin = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True)
mannequin.match(X, y)
print("Intercept:", mannequin.intercept_)
print("Coefficients:", mannequin.coef_) Output:
- ntercept (15) represents the common gross sales for the baseline class (Chocolate).
- Strawberry coefficient (-5) means Strawberry sells 5 items lower than Chocolate.
- Vanilla coefficient (-3) means Vanilla sells 3 items lower than Chocolate.
Every coefficient exhibits the impact of a class relative to the baseline, leading to steady and interpretable outputs with out multicollinearity.
Finest Practices and Takeaways
As soon as you might be conscious of the lure of the dummy variable, it is going to be easy to keep away from it. Comply with one easy rule. When a categorical function has ok classes, then solely ok -1 dummy variables are used.
The class that you simply omit seems to be the reference class. All different classes are paralleled to it. This eliminates the perfect multicollinearity that might happen in case they’re all included.
That is principally finished proper with the help of most trendy instruments. Pandas has the drop_first=True choice in get_dummies, which is able to mechanically drop one dummy column. The OneHotEncoder of scikit study additionally has a drop parameter that may be utilised to do that safely. Most statistical packages, e.g., R or statsmodels, mechanically omit one class in case a mannequin has an intercept.
Nonetheless, you might be suggested to be aware of your instruments. Everytime you generate dummy variables manually, you’ll want to drop one of many classes your self.
The elimination of 1 dummy is feasible because it eliminates redundancy. It units a baseline. The opposite coefficients have now displayed the distinction between every class and that baseline. No info is misplaced. Within the case of all of the dummy values being 0, a given commentary is within the reference class.
The important thing takeaway is straightforward. Categorical knowledge will be enormously included into regression fashions utilizing dummy variables. By no means have a couple of much less dummy than the variety of classes. This ensures that your mannequin is steady, interpretable and doesn’t have multicollinearity as a consequence of redundant variables.
Conclusion
Dummy variables are a vital useful resource to cope with categorical knowledge in machine studying fashions that want numbers. They allow representatives of classes to look inside right or acceptable sense with none which means of false order. Nonetheless, a dummy variable that makes use of an intercept and a dummy variable created upon every class outcomes to the dummy variable lure. It will end in good multicollinearity, such {that a} variable might be redundant, and the mannequin will be unable to decide distinctive coefficients.
The answer is straightforward. When there are ok classes of a function, then solely ok -1 dummy variables ought to be used. The omitted class takes the type of the baseline. This eliminates duplication, maintains the mannequin fixed and outcomes are readily interpreted.
If you wish to study all of the fundamentals of Machine Studying, checkout our Introduction to AI/ML FREE course!
Regularly Requested Questions
A. The dummy variable lure happens when all classes of a categorical variable are encoded as dummy variables whereas additionally together with an intercept in a regression mannequin. This creates good multicollinearity, making one dummy variable redundant and stopping the mannequin from estimating distinctive coefficients.
A. No. The dummy variable lure primarily impacts linear fashions comparable to linear regression, logistic regression, and fashions that depend on matrix inversion. Tree-based fashions like resolution timber, random forests, and gradient boosting are typically not affected.
A. If a categorical function has ok classes, you need to create ok − 1 dummy variables. The omitted class turns into the reference or baseline class, which helps keep away from multicollinearity.
A. You possibly can keep away from the dummy variable lure by dropping one dummy column throughout encoding. In pandas, this may be finished utilizing get_dummies(..., drop_first=True). In scikit-learn, the OneHotEncoder has a drop parameter that serves the identical goal.
A. The reference class is the class whose dummy variable is omitted throughout encoding. When all dummy variables are 0, the commentary belongs to this class. All mannequin coefficients are interpreted relative to this baseline.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.