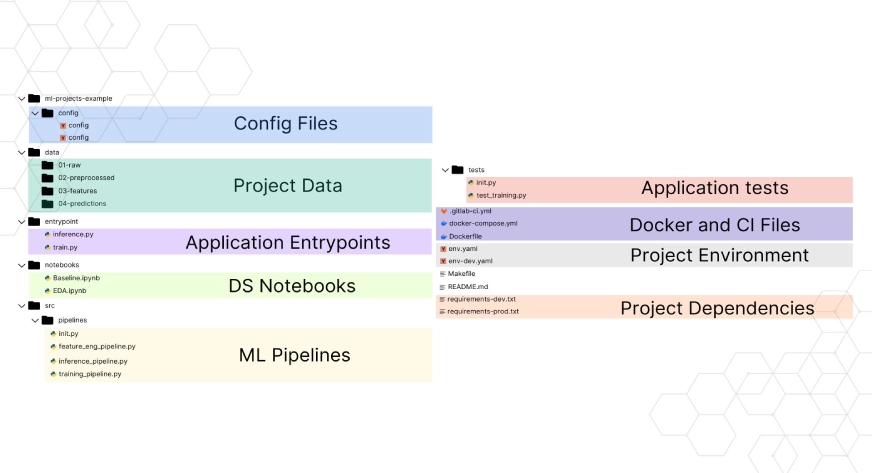
Ever felt misplaced in messy folders, so many scripts, and unorganized code? That chaos solely slows you down and hardens the info science journey. Organized workflows and mission buildings aren’t simply nice-to-have, as a result of it impacts the reproducibility, collaboration and understanding of what’s taking place within the mission. On this weblog, we’ll discover the most effective practices plus have a look at a pattern mission to information your forthcoming tasks. With none additional ado let’s look into a few of the necessary frameworks, frequent practices, how to enhance them.
Common Knowledge Science Workflow Frameworks for Undertaking Construction
Knowledge science frameworks present a structured method to outline and preserve a transparent knowledge science mission construction, guiding groups from downside definition to deployment whereas enhancing reproducibility and collaboration.
CRISP-DM
CRISP-DM is the acronym for Cross-Business Course of for Knowledge Mining. It follows a cyclic iterative construction together with:
- Enterprise Understanding
- Knowledge Understanding
- Knowledge Preparation
- Modeling
- Analysis
- Deployment
This framework can be utilized as a typical throughout a number of domains, although the order of steps of it may be versatile and you’ll transfer again in addition to against the unidirectional circulation. We’ll have a look at a mission utilizing this framework in a while on this weblog.
OSEMN
One other in style framework on the earth of knowledge science. The concept right here is to interrupt the complicated issues into 5 steps and clear up them step-by-step, the 5 steps of OSEMN (pronounced as Superior) are:
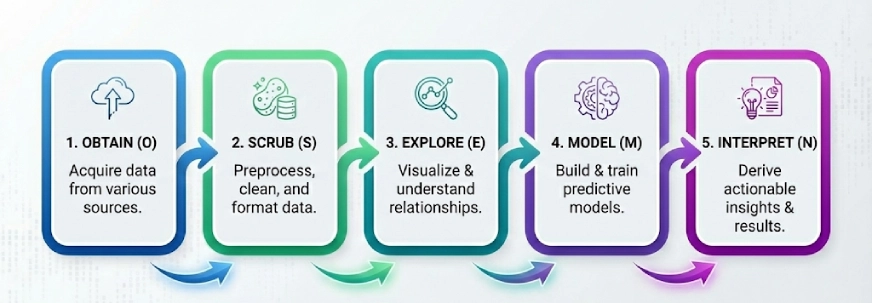
- Acquire
- Scrub
- Discover
- Mannequin
- Interpret
Word: The ‘N’ in “OSEMN” is the N in iNterpret.
We comply with these 5 logical steps to “Acquire” the info, “Scrub” or preprocess the info, then “Discover” the info by utilizing visualizations and understanding the relationships between the info, after which we “Mannequin” the info to make use of the inputs to foretell the outputs. Lastly, we “Interpret” the outcomes and discover actionable insights.
KDD
KDD or Data Discovery in Databases consists of a number of processes that goal to show uncooked knowledge into information discovery. Listed below are the steps on this framework:

- Choice
- Pre-Processing
- Transformation
- Knowledge Mining
- Interpretation/Analysis
It’s value mentioning that individuals consult with KDD as Knowledge Mining, however Knowledge Mining is the particular step the place algorithms are used to seek out patterns. Whereas, KDD covers all the lifecycle from the beginning to finish.
SEMMA
This framework emphasises extra on the mannequin growth. The SEMMA comes from the logical steps within the framework that are:
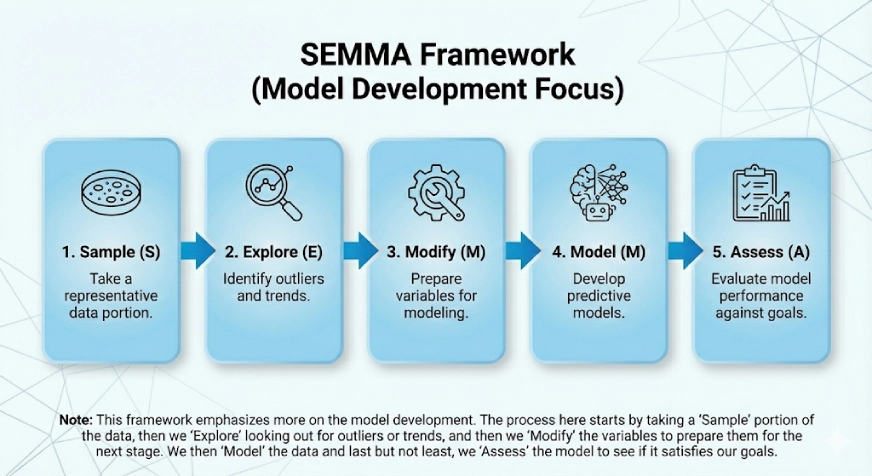
- Pattern
- Discover
- Modify
- Mannequin
- Assess
The method right here begins by taking a “Pattern” portion of the info, then we “Discover” searching for outliers or traits, after which we “Modify” the variables to arrange them for the subsequent stage. We then “Mannequin” the info and final however not least, we “Assess” the mannequin to see if it satisfies our targets.
Widespread Practices that Must be Improved
Enhancing these practices is important for sustaining a clear and scalable knowledge science mission construction, particularly as tasks develop in measurement and complexity.
1. The issue with “Paths”
Folks usually hardcode absolute paths like pd.read_csv(“C:/Customers/Identify/Downloads/knowledge.csv”). That is effective whereas testing issues out on Jupyter Pocket book however when used within the precise mission it breaks the code for everybody else.
The Repair: All the time use relative paths with the assistance of libraries like “os” or “pathlib”. Alternatively, you may select so as to add the paths in a config file (as an example: DATA_DIR=/residence/ubuntu/path).
2. The Cluttered Jupyter Pocket book
Generally folks use a single Jupyter Pocket book with 100+ cells containing imports, EDA, cleansing, modeling, and visualization. This is able to make it unattainable to check or model management.
The Repair: Use Jupyter Notebooks just for Exploration and keep on with Python Scripts for Automation. As soon as a cleansing perform works, add it to a src/processing.py file after which you may import it into the pocket book. This provides modularity and re-usability and in addition makes testing and understanding the pocket book so much easier.
3. Model the Code not the Knowledge
Git can battle in dealing with giant CSV recordsdata. Folks on the market usually push knowledge to GitHub which may take loads of time and in addition trigger different issues.
The Repair: Point out and use Knowledge Model Management (DVC in brief). It’s like Git however for knowledge.
4. Not offering a README for the mission
A repository can comprise nice code however with out directions on how you can set up dependencies or run the scripts might be chaotic.
The Repair: Make sure that you at all times craft a very good README.md that has data on Easy methods to arrange the setting, The place and how you can get the info, How to run the mannequin and different necessary scripts.
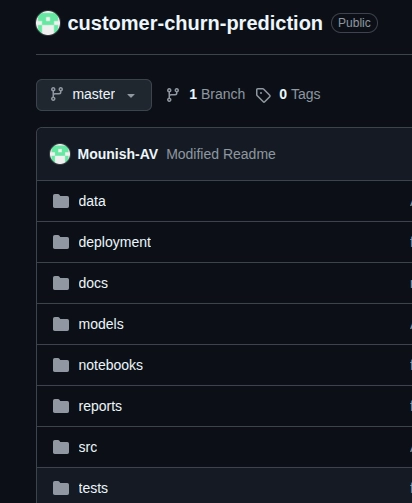
Constructing a Buyer Churn Prediction System [Sample Project]
Now utilizing the CRISP-DM framework I’ve created a pattern mission known as “Buyer Churn Prediction System”, let’s perceive the complete course of and the steps by taking a greater have a look at the identical.
Right here’s the GitHub hyperlink of the repository.
Word: This can be a pattern mission and is crafted to know how you can implement the framework and comply with a typical process.
Making use of CRISP-DM Step by Step
- Enterprise Understanding: Right here we should outline what we’re really making an attempt to unravel. In our case it’s recognizing clients who’re more likely to churn. We set clear targets for the system, 85%+ accuracy and 80%+ recall, and the enterprise purpose right here is to retain the purchasers.
- Knowledge Understanding In our case the Telco Buyer Churn dataset. We’ve got to look into the descriptive statistics, verify the info high quality, search for lacking values (additionally take into consideration how we are able to deal with them), additionally we’ve got to see how the goal variable is distributed, additionally lastly we have to discover the correlations between the variables to see what options matter.
- Knowledge Preparation: This step can take time however must be completed fastidiously. Right here we cleanse the messy knowledge, take care of the lacking values and outliers, create new options if required, encode the specific variables, break up the dataset into coaching (70%), validation (15%), and take a look at (15%), and at last normalizing the options for our fashions.
- Modeling: In this important step, we begin with a easy mannequin or baseline (logistic regression in our case), then experiment with different fashions like Random Forest, XGBoost to realize our enterprise targets. We then tune the hyperparameters.
- Analysis: Right here we work out which mannequin is working the most effective for us and is assembly our enterprise targets. In our case we have to have a look at the precision, recall, F1-scores, ROC-AUC curves and the confusion matrix. This step helps us decide the ultimate mannequin for our purpose.
- Deployment: That is the place we really begin utilizing the mannequin. Right here we are able to use FastAPI or every other options, containerize it with Docker for scalability, and set-up monitoring for observe functions.
Clearly utilizing a step-by-step course of helps present a transparent path to the mission, additionally through the mission growth you may make use of progress trackers and GitHub’s model controls can absolutely assist. Knowledge Preparation wants intricate care because it received’t want many revisions if rightly completed, if any challenge arises after deployment it may be mounted by going again to the modeling section.
Conclusion
As talked about within the begin of the weblog, organized workflows and mission buildings aren’t simply nice-to-have, they’re a should. With CRISP-DM, OSEMN, KDD, or SEMMA, a step-by-step course of retains tasks clear and reproducible. Additionally don’t overlook to make use of relative paths, hold Jupyter Notebooks for Exploration, and at all times craft a very good README.md. All the time keep in mind that growth is an iterative course of and having a transparent structured framework to your tasks will ease your journey.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
A. Reproducibility in knowledge science means having the ability to get hold of the identical outcomes utilizing the identical dataset, code, and configuration settings. A reproducible mission ensures that experiments might be verified, debugged, and improved over time. It additionally makes collaboration simpler, as different group members can run the mission with out inconsistencies brought on by setting or knowledge variations.
A. Mannequin drift happens when a machine studying mannequin’s efficiency degrades as a result of real-world knowledge modifications over time. This could occur attributable to modifications in person conduct, market situations, or knowledge distributions. Monitoring for mannequin drift is important in manufacturing techniques to make sure fashions stay correct, dependable, and aligned with enterprise goals.
A. A digital setting isolates mission dependencies and prevents conflicts between completely different library variations. Since knowledge science tasks usually depend on particular variations of Python packages, utilizing digital environments ensures constant outcomes throughout machines and over time. That is important for reproducibility, deployment, and collaboration in real-world knowledge science workflows.
A. A knowledge pipeline is a sequence of automated steps that transfer knowledge from uncooked sources to a model-ready format. It usually consists of knowledge ingestion, cleansing, transformation, and storage.
Login to proceed studying and luxuriate in expert-curated content material.