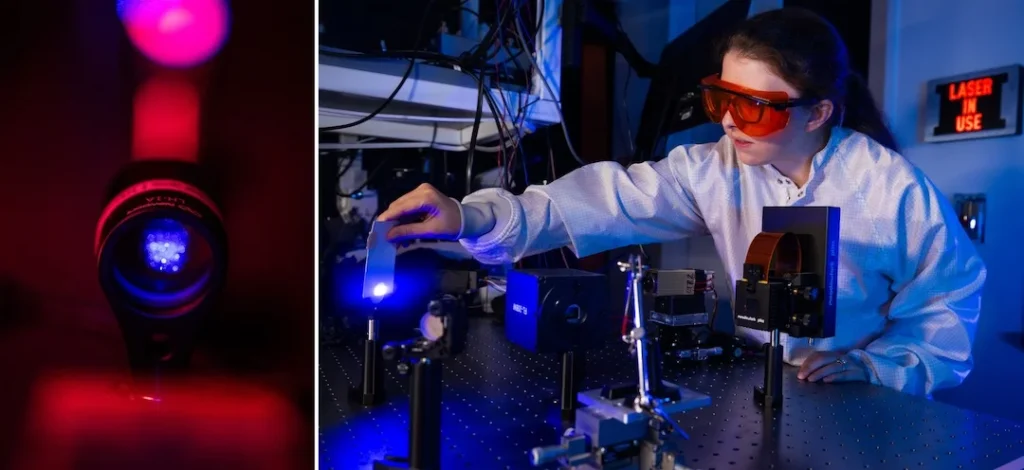
Photograph credit score: Jeff Fitlow/Rice College
By Silvia Cernea Clark
Researchers at Rice College have developed a tender robotic arm able to performing advanced duties corresponding to navigating round an impediment or hitting a ball, guided and powered remotely by laser beams with none onboard electronics or wiring. The analysis might inform new methods to regulate implantable surgical gadgets or industrial machines that have to deal with delicate objects.
In a proof-of-concept examine that integrates good supplies, machine studying and an optical management system, a group of Rice researchers led by supplies scientist Hanyu Zhu used a light-patterning system to exactly induce movement in a robotic arm constructed from azobenzene liquid crystal elastomer ⎯ a sort of polymer that responds to mild.
In keeping with the examine revealed in Superior Clever Methods, the brand new robotic system incorporates a neural community skilled to foretell the precise mild sample wanted to create particular arm actions. This makes it simpler for the robotic to execute advanced duties while not having equally advanced enter from an operator.
“This was the primary demonstration of real-time, reconfigurable, automated management over a light-responsive materials for a tender robotic arm,” mentioned Elizabeth Blackert, a Rice doctoral alumna who’s the primary creator on the examine.
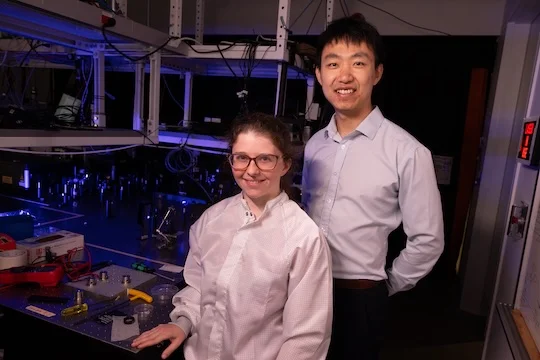 Elizabeth Blackert and Hanyu Zhu (Photograph credit score: Jeff Fitlow/Rice College).
Elizabeth Blackert and Hanyu Zhu (Photograph credit score: Jeff Fitlow/Rice College).
Standard robots sometimes contain inflexible buildings with cellular components like hinges, wheels or grippers to allow a predefined, comparatively constrained vary of movement. Comfortable robots have opened up new areas of software in contexts like medication, the place safely interacting with delicate objects is required. So-called continuum robots are a sort of sentimental robotic that forgoes mobility constraints, enabling adaptive movement with a vastly expanded diploma of freedom.
“A serious problem in utilizing tender supplies for robots is they’re both tethered or have quite simple, predetermined performance,” mentioned Zhu, assistant professor of supplies science and nanoengineering. “Constructing remotely and arbitrarily programmable tender robots requires a singular mix of experience involving supplies growth, optical system design and machine studying capabilities. Our analysis group was uniquely suited to tackle this interdisciplinary work.”
The group created a brand new variation of an elastomer that shrinks beneath blue laser mild then relaxes and regrows at the hours of darkness ⎯ a characteristic generally known as quick rest time that makes real-time management attainable. In contrast to different light-sensitive supplies that require dangerous ultraviolet mild or take minutes to reset, this one works with safer, longer wavelengths and responds inside seconds.
“After we shine a laser on one aspect of the fabric, the shrinking causes the fabric to bend in that route,” Blackert mentioned. “Our materials bends towards laser mild like a flower stem does towards daylight.”
To manage the fabric, the researchers used a spatial mild modulator to separate a single laser beam into a number of beamlets, every directed to a distinct a part of the robotic arm. The beamlets will be turned on or off and adjusted in depth, permitting the arm to bend or contract at any given level, very similar to the tentacles of an octopus. This system can in precept create a robotic with just about infinite levels of freedom ⎯ far past the capabilities of conventional robots with fastened joints.
“What’s new right here is utilizing the sunshine sample to realize advanced adjustments in form,” mentioned Rafael Verduzco, professor and affiliate chair of chemical and biomolecular engineering and professor of supplies science and nanoengineering. “In prior work, the fabric itself was patterned or programmed to alter form in a technique, however right here the fabric can change in a number of methods, relying on the laser beamlet sample.”
To coach such a multiparameter arm, the group ran a small variety of combos of sunshine settings and recorded how the robotic arm deformed in every case, utilizing the info to coach a convolutional neural community ⎯ a sort of synthetic intelligence utilized in picture recognition. The mannequin was then in a position to output the precise mild sample wanted to create a desired form corresponding to flexing or a reach-around movement.
The present prototype is flat and strikes in 2D, however future variations might bend in three dimensions with extra sensors and cameras.
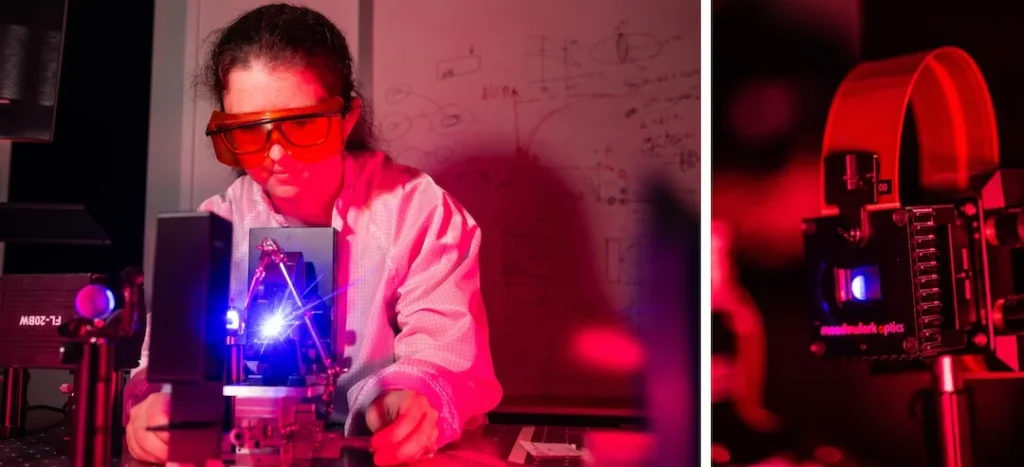 Photograph credit score: Jeff Fitlow/Rice College
Photograph credit score: Jeff Fitlow/Rice College
“This can be a step in direction of having safer, extra succesful robotics for varied purposes starting from implantable biomedical gadgets to industrial robots that deal with tender items,” Blackert mentioned.

Rice College