- January 21, 2018
- Vasilis Vryniotis
- . 1 Remark
Deep Studying (the favorite buzzword of late 2010s together with blockchain/bitcoin and Knowledge Science/Machine Studying) has enabled us to do some actually cool stuff the previous few years. Apart from the advances in algorithms (which admittedly are primarily based on concepts already recognized since Nineteen Nineties aka “Knowledge Mining period”), the primary causes of its success will be attributed to the supply of huge free datasets, the introduction of open-source libraries and the usage of GPUs. On this weblog submit I’ll deal with the final two and I’ll share with you some ideas that I discovered the exhausting approach.
Why TensorFlow & Keras?
TensorFlow is a very fashionable Deep Studying library developed by Google which lets you prototype shortly advanced networks. It comes with a number of attention-grabbing options resembling auto-differentiation (which saves you from estimating/coding the gradients of the price features) and GPU help (which lets you get simply a 200x pace enchancment utilizing respectable {hardware}). Furthermore it provides a Python interface which suggests you can prototype shortly with out requiring to write down C or CUDA code. Admittedly there are many different frameworks one can use as an alternative of TensorFlow, resembling Torch, MXNet, Theano, Caffe, Deeplearning4j, CNTK, and so on nevertheless it all boils all the way down to your use-case and your private choice.
However why Keras? For me utilizing immediately TF is like doing Machine Studying with Numpy. Sure it’s possible and infrequently it’s important to do it (particularly should you write customized layers/loss-functions) however do you actually wish to write code that describes the advanced networks as a sequence of vector operations (sure, I do know there are higher-level strategies in TF however they don’t seem to be as cool as Keras)? Additionally what if you wish to transfer to a unique library? Nicely you then would most likely must rewrite the code, which sucks. Ta ta taaa, Keras to the rescue! Keras permits you to describe your networks utilizing excessive stage ideas and write code that’s backend agnostic, which means you can run the networks throughout completely different deep studying libraries. Few issues I like about Keras is that it’s well-written, it has an object oriented structure, it’s straightforward to contribute and it has a pleasant neighborhood. Should you prefer it, say thanks to François Chollet for creating it and open-sourcing it.
Ideas and Gotchas for Multi-GPU coaching
With out additional ado, let’s leap to some recommendations on methods to benefit from GPU coaching on Keras and a few gotchas that it’s best to take into account:
1. Multi-GPU coaching shouldn’t be computerized
Coaching fashions on GPU utilizing Keras & Tensorflow is seamless. When you have an NVIDIA card and you’ve got put in CUDA, the libraries will robotically detect it and use it for coaching. So cool! However what in case you are a spoilt brat and you’ve got a number of GPUs? Nicely sadly you’ll have to work a bit to realize multi-GPU coaching.
There are a number of methods to parallelise a community relying on what you wish to obtain however the primary two approaches is mannequin and knowledge parallelization. The primary will help you in case your mannequin is simply too advanced to slot in a single GPU whereas the latter helps once you wish to pace up the execution. Usually when folks discuss multi-GPU coaching they imply the latter. It was once tougher to realize however fortunately Keras has not too long ago included a utility technique known as mutli_gpu_model which makes the parallel coaching/predictions simpler (at the moment solely accessible with TF backend). The principle concept is that you just move your mannequin by way of the strategy and it’s copied throughout completely different GPUs. The unique enter is break up into chunks that are fed to the assorted GPUs after which they’re aggregated as a single output. This technique can be utilized for attaining parallel coaching and predictions, nonetheless remember the fact that for coaching it doesn’t scale linearly with the quantity of GPUs because of the required synchronization.
2. Take note of the Batch Dimension
Once you do multi-GPU coaching take note of the batch dimension because it has a number of results on pace/reminiscence, convergence of your mannequin and in case you are not cautious you would possibly corrupt your mannequin weights!
Velocity/reminiscence: Clearly the bigger the batch the sooner the coaching/prediction. It is because there’s an overhead on placing in and taking out knowledge from the GPUs, so small batches have extra overhead. On the flip-side, the bigger the batch the extra reminiscence you want within the GPU. Particularly throughout coaching, the inputs of every layer are stored in reminiscence as they’re required on the back-propagation step, so rising your batch dimension an excessive amount of can result in out-of-memory errors.
Convergence: Should you use Stochastic Gradient Respectable (SGD) or a few of its variants to coach your mannequin, it’s best to take into account that the batch dimension can have an effect on the power of your community to converge and generalize. Typical batch sizes in lots of laptop imaginative and prescient issues are between 32-512 examples. As Keskar et al put it, “It has been noticed in observe that when utilizing a bigger batch (than 512) there’s a degradation within the high quality of the mannequin, as measured by its capability to generalize.”. Word that different completely different optimizers have completely different properties and specialised distributed optimization strategies will help with the issue. If you’re within the mathematical particulars, I like to recommend studying Joeri Hermans’ Thesis “On Scalable Deep Studying and Parallelizing Gradient Descent”.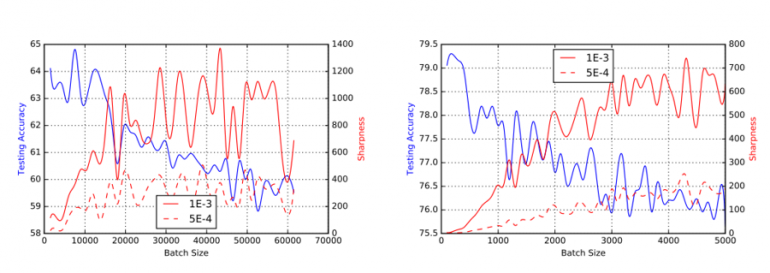
Corrupting the weights: It is a nasty technical element which might have devastating outcomes. Once you do multi-GPU coaching, you will need to feed all of the GPUs with knowledge. It might occur that the final batch of your epoch has much less knowledge than outlined (as a result of the dimensions of your dataset cannot be divided precisely by the dimensions of your batch). This would possibly trigger some GPUs to not obtain any knowledge over the last step. Sadly some Keras Layers, most notably the Batch Normalization Layer, can’t deal with that resulting in nan values showing within the weights (the operating imply and variance within the BN layer). To make the issues even nastier, one won’t observe the issue throughout coaching (whereas studying section is 1) as a result of the particular layer makes use of the batch’s imply/variance within the estimations. Nonetheless throughout predictions (studying section set to 0), the operating imply/variance is used which in our case can grow to be nan resulting in poor outcomes. So do your self a favour and all the time guarantee that your batch dimension is fastened once you do multi-GPU coaching. Two easy methods to realize that is both by rejecting batches that don’t match the predefined dimension or repeat the information inside the batch till you attain the predefined dimension. Final however not least remember the fact that in a multi-GPU setup, the batch dimension ought to be a a number of of the variety of accessible GPUs in your system.
3. GPU knowledge Hunger aka the CPUs can’t sustain with the GPUs
Usually the most costly half whereas coaching/predicting Deep networks is the estimation that occurs on the GPUs. The info are preprocessed within the CPUs on the background and they’re fed to the GPUs periodically. Nonetheless one shouldn’t underestimate how briskly the GPUs are; it may occur that in case your community is simply too shallow or the preprocessing step is simply too advanced that your CPUs can’t sustain along with your GPUs or in different phrases they don’t feed them with knowledge shortly sufficient. This could result in low GPU utilization which interprets to wasted cash/sources.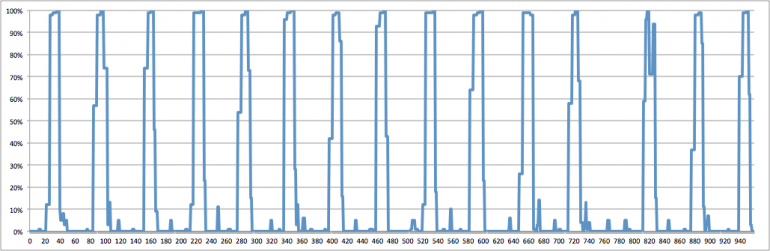
Keras usually performs the estimations of the batches in parallel nonetheless attributable to Python’s GIL (World Interpreter Lock) you possibly can’t actually obtain true multi-threading in Python. There are two options for that: both use a number of processes (be aware that there are many gotchas on this one which I’m not going to cowl right here) or preserve your preprocessing step easy. Previously I’ve despatched a Pull-Request on Keras to alleviate a number of the pointless pressure that we have been placing on the CPUs throughout Picture preprocessing, so most customers shouldn’t be affected in the event that they use the usual mills. When you have customized mills, attempt to push as a lot logic as potential to C libraries resembling Numpy as a result of a few of these strategies really launch the GIL which suggests you can improve the diploma of parallelization. A great way to detect whether or not you might be dealing with GPU knowledge hunger is to watch the GPU utilization, nonetheless be warned that this isn’t the one motive for observing that (the synchronization that occurs throughout coaching throughout the a number of GPUs can be accountable for low utilization). Usually GPU knowledge hunger will be detected by observing GPU bursts adopted by lengthy pauses with no utilization. Previously I’ve open-sourced an extension for Dstat that may enable you measure your GPU utilization, so take a look on the unique weblog submit.
4. Saving your parallel fashions
Say you used the mutli_gpu_model technique to parallelize your mannequin, the coaching completed and now you wish to persist its weights. The unhealthy information is you can’t simply name save() on it. Presently Keras has a limitation that doesn’t help you save a parallel mannequin. There are 2 methods round this: both name the save() on the reference of the unique mannequin (the weights shall be up to date robotically) or it’s good to serialize the mannequin by chopping-down the parallelized model and cleansing up all of the pointless connections. The primary choice is approach simpler however on the longer term I plan to open-source a serialize() technique that performs the latter.
5. Counting the accessible GPUs has a nasty side-effect
Sadly in the intervening time, there’s a nasty side-effect on the tensorflow.python.shopper.device_lib.list_local_devices() technique which causes a brand new TensorFlow Session to be created and the initialization of all of the accessible GPUs on the system. This could result in surprising outcomes resembling viewing extra GPUs than specified or prematurely initializing new classes (you possibly can learn all the small print on this pull-request). To keep away from comparable surprises you might be suggested to make use of Keras’ Ok.get_session().list_devices() technique as an alternative, which is able to return you all of the at the moment registered GPUs on the session. Final however not least, remember the fact that calling the list_devices() technique is one way or the other costly, so in case you are simply on the variety of accessible GPUs name the strategy as soon as and retailer their quantity on a neighborhood variable.
That’s it! Hope you discovered this record helpful. Should you discovered different gotchas/ideas for GPU coaching on Keras, share them under on the feedback. 🙂

