At the moment we’ll be taught in regards to the SQL IN operator. The RDBMS programs are very fashionable immediately by way of knowledge storage, knowledge safety, and knowledge evaluation. SQL stands for Structured Question Language which is used to create, replace, or retrieve knowledge in RDBMS or Relational Database Administration Programs like SQL Server, Oracle, Microsoft Entry, MySQL, and PostgreSQL.
After we question or retrieve knowledge from a SQL database, we filter data in numerous methods in order that they’ll meet the appliance’s necessities. The SQL IN operator can be utilized with SQL databases like SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and different RDBMS programs.
Whereas writing SQL queries you collect all of the enterprise necessities to write down advanced SQL statements. SQL Supplies numerous operators to question the information from the database. An operator is a reserved key phrase that’s used within the question in order that it might probably generate particular output for the appliance. To make use of the operators throughout the question, we use the The place clause, then operators (e.g., SQL IN Operator) can be utilized to outline a number of circumstances.
Introduction
SQL the place clause is used to filter the information from a question, numerous operators can be utilized within the the place clause. By utilizing an operator, you possibly can outline particular circumstances to retrieve outcomes from the database and a number of circumstances may also be outlined utilizing operators. There are a lot of helpful operators out there in SQL like Arithmetic Operators, Comparability Operators, and Logical Operators, we’ll give attention to SQL IN operator in immediately’s article. SQL IN operator is among the most typical operators used within the the place clause to specify a number of values or within the subquery in order that the output can meet the requirement.
Syntax
Allow us to focus on the SQL IN operator syntax under:
SELECT column1, column2, FROM desk the place expressions IN (value1, value2, value3… so on)
Or
SELECT column1, column2, FROM desk the place expressions IN (SELECT statements)
Parameters
expressions or statements
That is the worth or column title to judge
value1, value2, value3… so on
These values are checked in opposition to the expression. If a number of values match the expression then the IN operator evaluates to true.
expressions IN (SELECT statements)
The outcome set of those choose statements shall be examined in opposition to expressions. If any of the values within the outcome set match expression, then the IN operator will consider to True.
Now we’ll focus on just a few examples of the SQL IN operator with the intention to perceive it higher. The IN operator works with numerous knowledge sorts together with Strings, Numbers, and Dates. I’ll present examples of various use circumstances of IN operator.
IN Operator with Strings
The SQL IN operator works with String columns which have knowledge sorts char, nchar, varchar, or nvarchar. We’re utilizing the Journey Works pattern database on this article. In case you have not already put in the Journey Works database, you possibly can obtain and set up it earlier than utilizing the under question pattern. On this question, I used the Particular person.Tackle desk and used the Metropolis column within the The place clause to filter with worth ‘Bothell’, it’s good to use a single quote for string worth :
|
SELECT TOP 10 AddressLine1, Metropolis, PostalCode FROM Particular person.Tackle WHERE Metropolis IN (‘Bothell’)
|
The output is under, the Metropolis column filtered with worth ‘Bothell’:
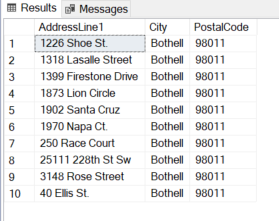
IN Operator with Numbers
The SQL IN operator additionally works with columns which have an information kind. Within the under question I used the SalesOrderHeader desk and the SalesOrderID column has a numeric worth. The question is filtered for SalesOrderID 43660 and 43661:
|
SELECT SalesOrderID,CustomerID,TotalDue FROM Gross sales.SalesOrderHeader WHERE SalesOrderID IN (43660,43661)
|
The output exhibits solely outcomes for these two SalesOrderID.:
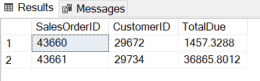

IN Operator with Dates
Typically we have to filter knowledge based mostly on date values in particular columns and IN operator works completely with any date column or values. Allow us to perceive under instance:
|
SELECT [SpecialOfferID],[Description],[DiscountPct],[StartDate] FROM [Sales].[SpecialOffer] The place StartDate IN (‘2011-05-01 00:00:00.000’,‘2012-04-13 00:00:00.000’)
|
Within the above instance question now we have used the SpecialOffer desk which has the date column StartDate which is used within the SQL IN operator with two values ‘2011-05-01 00:00:00.000’ and ‘2012-04-13 00:00:00.000’. It’s essential use a single quote for the date worth.
The output exhibits the filtered outcome as anticipated:
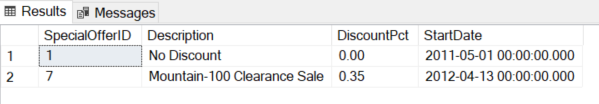

Exchange a number of OR circumstances with SQL IN Operator
The IN Operator is used to interchange a number of OR circumstances. To grasp this allow us to take an instance under. Within the first question under, I used the Particular person desk, and within the The place clause filtered for the FirstName column which was used two occasions mixed with the OR situation, on the first question under the FirstName has the worth ‘Kim’ and the second Firstname has worth ‘Sam’:
|
SELECT FirstName,LastName FROM Particular person.Particular person WHERE FirstName =‘Kim’ or FirstName =‘Sam’
|
The above SQL statements may also be shortened utilizing IN operator as under:
|
SELECT FirstName, LastName FROM Particular person.Particular person WHERE FirstName IN (‘Kim’,‘Sam’)
|
The above question used the Particular person desk and the FirstName column is used within the IN operator, there are two values within the SQL IN operator ‘Kim’ and ‘Sam’. The output is exhibiting all outcomes which have FirstName both ‘Kim’ or ‘Sam’.
The output for each above queries is as under:
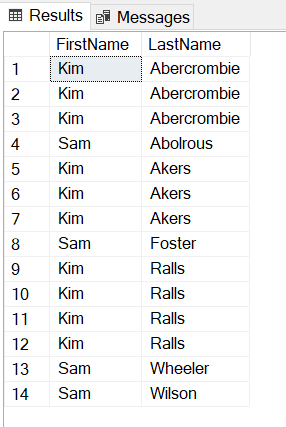

A number of IN Operator
We are able to use the SQL IN operator with the AND operator to examine circumstances with multiple column. Within the under instance, I used the Particular person desk and added FirstName and LastName within the the place clause, each the columns FirstName and LastName comprises SQL IN operator, so we will use a number of IN operator to construct advanced SQL logic:
|
SELECT FirstName, LastName FROM Particular person.Particular person WHERE FirstName IN (‘Kim’,’Sam’) AND LastName IN (‘Foster’,’Akers’)
|
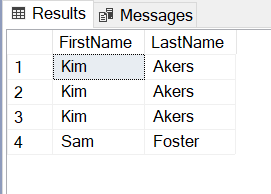

IN with Subquery
Within the above examples we used the static values within the IN operator, generally the values to filter within the SQL IN operator should not predefined for instance we could must retrieve the values from one other desk utilizing a choose question. On this case, we will use the subquery within the SQL IN operator to filter the dataset dynamically. Subquery provides you extra flexibility within the filter standards. The subquery within the IN operator additionally helps to mix two queries right into a single question. The subquery ought to include a single column within the choose statements and a number of columns should not allowed.
Within the under SQL question, the outer question retrieves knowledge from the SalesOrderDetail desk and the subquery is getting knowledge from the SalesOrderHeader desk:
|
SELECT [SalesOrderID],[OrderQty],[ProductID],[SpecialOfferID],[UnitPrice],[UnitPriceDiscount],[LineTotal] FROM [Sales].[SalesOrderDetail] WHERE SalesOrderID IN (SELECT SalesOrderID FROM [Sales].[SalesOrderHeader])
|
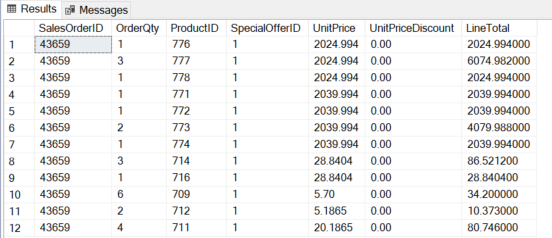

Nested IN Operator
We are able to additionally use the SQL IN operator inside one other IN operator. Allow us to see an instance under:
|
SELECT TOP 10 NAME, ProductNumber FROM [Production].[Product] WHERE ProductSubcategoryID IN (SELECT [ProductCategoryID] FROM [AdventureWorks2019].[Production].[ProductCategory] WHERE [ProductCategoryID] IN (1,2))
|
Within the above question, the outer question selects Identify and ProductNaumber from the Product desk which is filtered with ProductSubCategoryID from the subquery and the subquery additionally comprises an IN operator which is used to filter ProductCategoryID.
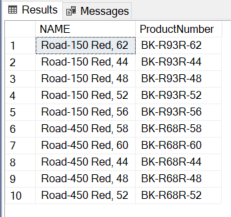

IN Operator duplicate values
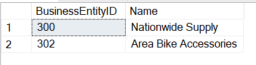
Duplicate values within the SQL IN operator are ignored. Allow us to perceive this by the under examples:
|
SELECT [BusinessEntityID],[Name] FROM [Sales].[Store] WHERE BusinessEntityID IN (300,302,300)
|
Within the above SQL statements, the IN operator comprises a reproduction worth of 300 and it’s ignored by the IN operator. The above SQL statements are the identical as these under:
|
SELECT [BusinessEntityID],[Name] FROM [Sales].[Store] WHERE BusinessEntityID IN (300,302,300)
|
The above question makes use of the Retailer desk and it’s exhibiting all of the rows which have Enterprise Entity ID 300 or 302. Each statements return the identical outcome as under:

NOT IN
Within the above examples, we wrote queries to incorporate data based mostly on the values within the SQL IN operator. Your question may give an output of 1000 data however you wish to reverse this time which implies you wish to exclude some data. We are able to use the NOT operator together with IN operator to indicate the outcomes that don’t match the required worth. We’ve got used IN operator to filter data within the above examples. Now we will use the NOT operator together with the SQL IN operator to filter data which aren’t matching with the supplied values. Allow us to see an instance under.
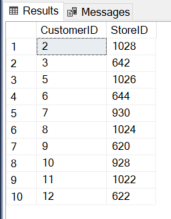
Within the under question we’re utilizing the Buyer desk and filtering knowledge based mostly on the StoreID column and the IN operator mixed with the NOT operator exhibits the outcome which isn’t matching with values 932 and 934:
|
SELECT TOP 10 CustomerID, StoreID from Gross sales.Buyer WHERE StoreID NOT IN (932,934)
|
The Output is under:

Conclusion
This text defined the SQL IN operator with numerous examples and use circumstances. The IN operator is used to filter knowledge for a specified set of values. It may also be used to interchange a number of OR circumstances. We are able to simplify advanced SQL to extra readable statements through the use of IN operator. We’ve got seen totally different knowledge sorts like Strings, Numbers, and Dates supported by IN operator.
Thanks for studying this text, please share your invaluable suggestions within the remark part.
