MySQL is taking a big step ahead by rethinking how international key constraints and cascades are managed. Beginning with MySQL 9.6, international key checks and cascade operations shall be dealt with immediately by the SQL engine reasonably than the InnoDB storage engine. This enchancment addresses long-standing challenges with change monitoring, binary log replication, and information consistency, making MySQL extra strong for heterogeneous environments, Change Information Seize (CDC) pipelines, and analytical workloads.
How Overseas Keys Beforehand Labored inside InnoDB
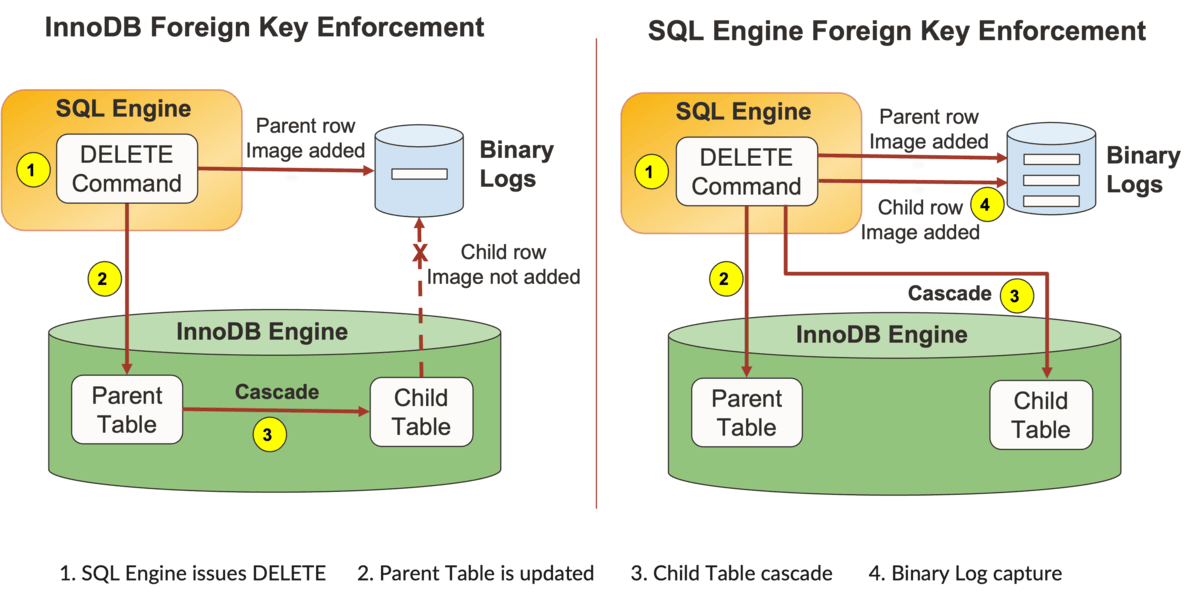
Traditionally, MySQL enforced international key constraints and cascades on the storage engine layer, particularly inside InnoDB. Right here’s the way it labored:
Overseas Key Cascades: When a press release like DELETE or UPDATE was executed on a guardian desk, InnoDB checked the international key constraints. If cascading actions (comparable to ON DELETE CASCADE) had been outlined, InnoDB dealt with updating or deleting the corresponding rows within the youngster desk.
Inner InnoDB Execution: All cascaded operations had been executed internally by InnoDB. The SQL engine initiated solely the guardian operation; each dependent motion on youngster tables was managed by InnoDB.
Importantly, these child-row modifications had been invisible to the SQL layer. Consequently, cascades carried out inside InnoDB didn’t seem within the MySQL binary log underneath row-based replication (RBR).
Operational Impression: As a result of these modifications had been hidden from the SQL engine and binary logs, downstream techniques, comparable to CDC pipelines and analytics platforms may miss them. This might result in inconsistent information, unreliable analytics, and replication points.
Limitations of InnoDB-Primarily based Overseas Keys
As MySQL deployments grew in scale and complexity, this legacy method revealed the next limitations:
- Hidden Information Adjustments: Cascading parent-child modifications carried out inside InnoDB had been invisible to the SQL layer and weren’t captured at the next stage.
- Incomplete System Logs: Baby row modifications had been typically lacking from binary logs, making replication and audits incomplete.
- Information Seize Gaps: Information instruments and downstream techniques counting on binary logs or a whole change historical past couldn’t at all times monitor each international key associated replace or delete.
- Replication Dangers: In advanced replication setups, these silent modifications may trigger information divergence between the first server and replicas, resulting in operational challenges.
The New Mannequin: SQL Engine-Managed Overseas Key Enforcement
To deal with these points, MySQL now enforces international keys and manages cascades within the SQL engine itself. With this variation, all international key operations on each guardian and youngster tables are totally seen to the SQL layer.
Key Benefits:
- Full Logging: Each change, together with cascades, is now seen, auditable, and totally recorded within the binary logs.
- Dependable Replication: No extra hidden information modifications; replication is now extra reliable and correct.
- Higher Analytics: Information seize and analytics instruments now get a whole, real-time view of all information modifications.
- Basis for Innovation: This structure makes it simpler to increase international key help throughout storage engines and future replication and observability options.
Notice: For storage engines apart from InnoDB that help international keys, enforcement and cascade actions proceed to be managed on the respective storage engine.
Efficiency Comparability
We perceive that efficiency is a prime precedence for MySQL customers contemplating a shift in international key enforcement from InnoDB to the SQL engine. Intensive benchmarking throughout frequent transactional workloads confirms that SQL engine based mostly international key enforcement and cascade performs practically identically to the InnoDB method. The price of international key checks and cascades stays successfully unchanged, leading to no observable regression in throughput or latency.This makes the brand new implementation secure to undertake even in high-throughput and mission crucial deployments.
Backward Compatibility
The SQL Engine international key enforcement and cascade is designed for full backward compatibility, preserving the semantics and habits of InnoDB international key enforcement. Whereas the general person expertise stays unchanged, there are a number of deliberate enhancements and minor behavioural variations value noting:
- Error Messages: Whereas error codes proceed to match earlier releases, the particular error message textual content (together with international key names) could differ as a result of order during which checks are carried out.
- Auto-Increment Gaps: If a international key constraint fails, any tried insert increments the auto-increment counter, which can lead to worth gaps, matching customary MySQL habits.
- Statistics Up to date for Cascaded Rows: Row-level statistics (comparable to
delete_rows) are up to date to incorporate rows affected by cascading international keyf operations. This ensures system statistics precisely mirror all information modifications carried out by international key enforcement. - Stricter Collation Validation: If a international key cascade would cross incompatible collations, an express error is raised stopping silent information points and enhancing information integrity for customers.
Protected Adoption with a Constructed-In Fallback
For managed adoption, MySQL introduces a read-only startup variable, innodb_native_foreign_keys. This supplies a easy improve path and minimizes sudden modifications throughout model transitions. By default, this variable is about to FALSE, making SQL Engine based mostly international key enforcement the default habits. Throughout staging or early manufacturing rollout, chances are you’ll set this variable to TRUE to quickly revert to InnoDB’s native international key dealing with. This supplies a transparent operational fallback whereas validating the brand new SQL Engine habits.
Notice: This technique variable is meant to assist ease migration and shall be eliminated in a future launch because the MySQL neighborhood totally adopts SQL Engine based mostly international keys.
Abstract: Why This Change Issues
By shifting international key enforcement to the SQL engine, MySQL closes a long-standing architectural hole. This enchancment ensures that information modifications are at all times seen, logged, and replicated, making MySQL a stronger platform for contemporary, distributed, and compliant information environments.
General, for MySQL customers, this implies higher information consistency, extra dependable replication, and fewer surprises in analytics and compliance workflows with out sacrificing efficiency.
What’s Subsequent on the Roadmap
- Broader help for triggers on cascaded modifications.
- Overseas key enforcement for extra storage engines.