Simply as you wouldn’t train a toddler to journey a motorbike on a busy freeway, AI brokers want managed environments to be taught and enhance. The atmosphere shapes how an agent perceives the world, learns from expertise, and makes selections, whether or not it’s a self-driving automotive or a chatbot. Understanding these environments is crucial to constructing AI programs that work reliably. On this article, we discover the several types of environments in AI and why they matter.
What’s an Setting in AI
In AI, an atmosphere is a stage the place AI brokers carry out its position. Consider it as the whole ecosystem surrounding an clever system from which agent can sense, work together and be taught from. An atmosphere is the gathering of all exterior components and circumstances that an AI agent should navigate to attain its objective.
The agent interacts with this atmosphere via two important mechanisms: sensors and actuators. Sensors are the agent’s eyes and ears, they collect details about the present state of the atmosphere and supply enter to the agent’s decision-making system. Actuators, then again, are the agent’s arms and voice, they execute the agent’s choice and produce output that instantly have an effect on the atmosphere.
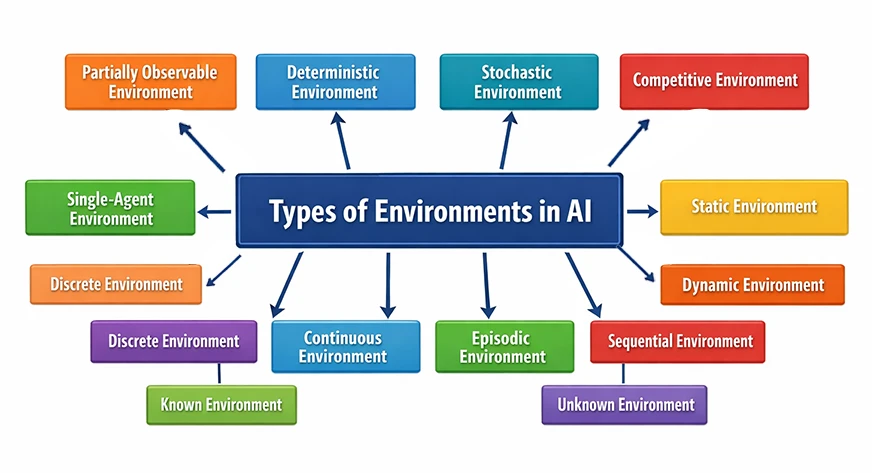
This all works in pairs: Totally vs Partially, Chaotic vs Secure, Deterministic vs Stochastic and so forth. That means, for each atmosphere that’s accessible there may be an reverse of it, additionally in use. Due to this fact, the kinds could be outlined in a comparative method.
Kinds of Environments in AI
1. Totally Observable vs Partially Observable Environments
Totally observable environments are these the place the AI agent has full visibility into the present state of the atmosphere. Each piece of data wanted to make an knowledgeable choice is available to the agent via its sensors. There are not any hidden surprises or lacking items of the puzzle.
Partially observable atmosphere is the alternative. The agent solely has incomplete details about the atmosphere’s present state. Essential particulars are hidden, making decision-making tougher as a result of the agent should work with uncertainty and incomplete data.
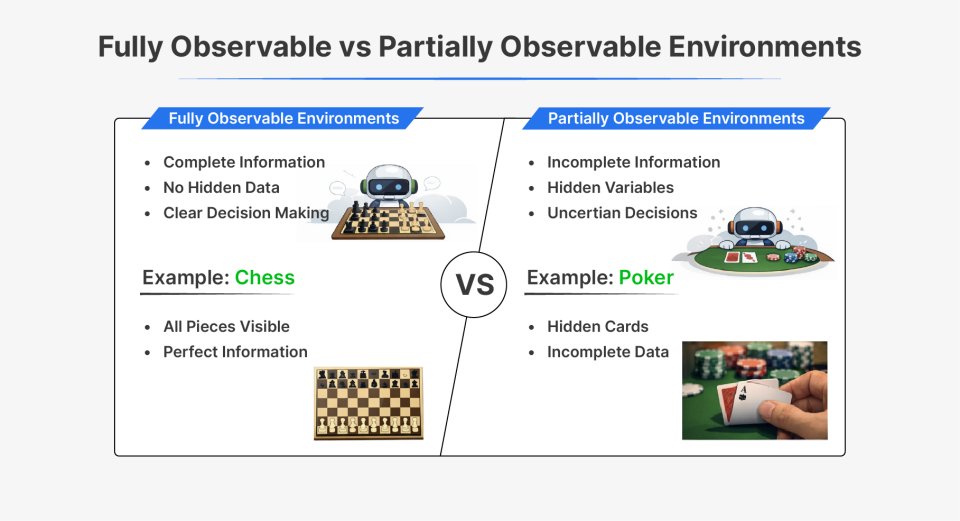
| Side | Totally Observable | Partially Observable |
|---|---|---|
| State visibility | Full entry to atmosphere state | Incomplete or hidden info |
| Choice certainty | Excessive | Low, requires inference |
| Instance | Chess | Poker |
2. Deterministic vs Stochastic Environments
Deterministic environments are totally predictable. When an agent takes an motion, the end result is at all times the identical and could be predicted with 100% certainty. There is no such thing as a randomness and variability, trigger and impact are completely corelated.
Stochastic atmosphere introduce randomness and uncertainity. The identical motion taken in equivalent circumstances would possibly produce completely different outcomes because of random components. This requires brokers to assume probabilistically and adapt to sudden outcomes.
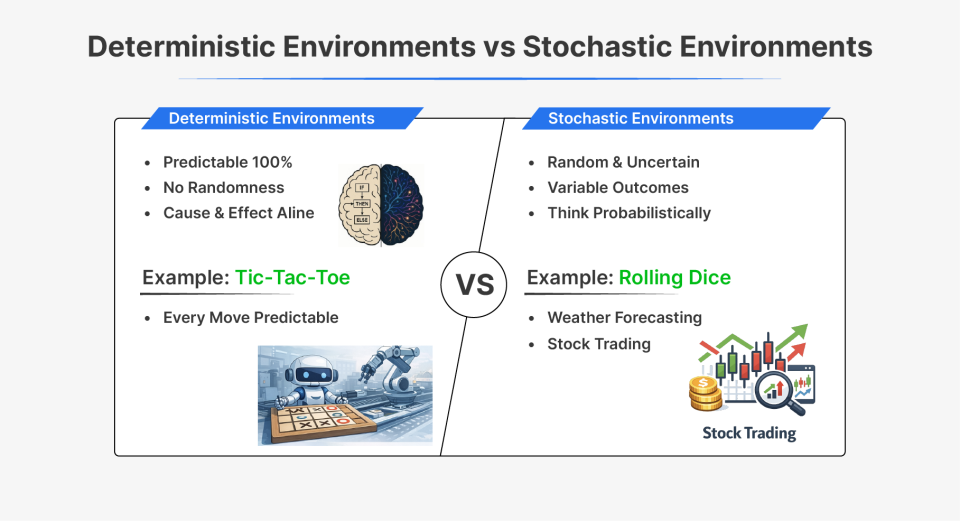
| Side | Deterministic | Stochastic |
|---|---|---|
| Final result predictability | Totally predictable | Includes randomness |
| Identical motion consequence | All the time similar | Can differ |
| Instance | Tic-Tac-Toe | Inventory market |
3. Aggressive vs Collaborative Environments
Aggressive environments function brokers working towards one another, typically opposing targets. When one agent wins, others lose, it’s a zero-sum dynamic the place success is relative.
Collaborative atmosphere function brokers working towards shared targets. Success is measured by collective achievements somewhat than particular person wins, and agent’s advantages from this cooperation.
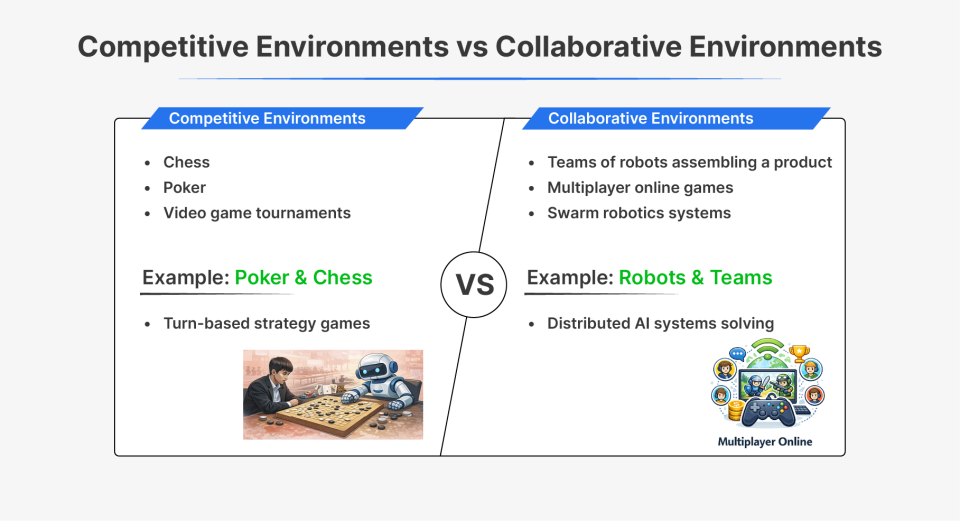
| Side | Aggressive | Collaborative |
|---|---|---|
| Agent targets | Conflicting | Shared |
| Final result nature | Zero-sum | Mutual profit |
| Instance | Chess | Robotic teamwork |
4. Single-Agent vs Multi-Agent Setting
Single-Agent atmosphere entails just one AI agent making selections and taking actions. The complexity comes from the atmosphere itself, not from interactions with different brokers.
Multi-Agent environments contain a number of AI brokers or mixture of AI and human brokers working concurrently, every making selections and influencing the general system. This will increase complexity as a result of brokers should think about not simply the atmosphere but additionally different agent’s behaviour and techniques.
| Side | Single-Agent | Multi-Agent |
|---|---|---|
| Variety of brokers | One | A number of |
| Interplay complexity | Low | Excessive |
| Instance | Sudoku solver | Autonomous visitors |
5. Static vs Dynamic Environments
Static environments stay unchanged except the agent acts. As soon as an motion is accomplished, the atmosphere waits for the following motion, it doesn’t evolve independently.
Dynamic environments change always, impartial of the agent’s actions. The atmosphere retains evolving, typically forcing the agent to adapt mid-action or mid plan.
| Side | Static | Dynamic |
|---|---|---|
| Setting change | Solely after agent acts | Modifications independently |
| Planning type | Lengthy-term planning | Steady adaptation |
6. Discrete vs Steady Environments
Discrete environments have finite, well-defined states and actions. Issues exist in distinct, separate classes with no values in between.
Steady Environments have infinite or near-infinite states and actions. Values circulate easily alongside a spectrum somewhat than leaping between distinct factors.
| Side | Discrete | Steady |
|---|---|---|
| State house | Finite | Infinite |
| Motion house | Countable | Steady vary |
7. Episodic vs Sequential Environments
Episodic environments break the agent’s interplay into impartial episodes or remoted situations. Every episode doesn’t considerably have an effect on future episodes, they’re successfully reset or impartial.
Sequential environments have occasions the place present choice instantly affect future conditions. The agent should assume long-term, understanding that at present’s selections create tomorrow’s challenges and alternatives.
| Side | Episodic | Sequential |
|---|---|---|
| Previous dependence | None | Sturdy |
| Planning horizon | Brief | Lengthy-term |
8. Recognized vs Unknown Environments
Recognized environments are these the place the agent has a whole mannequin or understanding of how the environments works, the foundations are recognized and stuck.
Unknown environments are these the place the agent should find out how the environments work via exploration and expertise, discovering guidelines, patterns, and cause-effect relationship dynamically.
| Side | Recognized | Unknown |
|---|---|---|
| Setting mannequin | Totally specified | Discovered via interplay |
| Studying requirement | Minimal | Important |
Why Setting Varieties Matter for AI Improvement
Understanding atmosphere sorts instantly affect the way you construct and prepare AI programs.
- Algorithm Choice: Deterministic environments enable actual algorithms; stochastic ones want probabilistic approaches.
- Coaching technique: Episodic environments enable impartial coaching samples; sequential ones want approaches that protect historical past and be taught sample over time.
- Scalability: Single-agent discrete environments are easier to scale than multi agent steady ones.
- Actual-World Testing: Simulated environments that precisely seize the goal atmosphere’s traits are essential for protected testing earlier than deploying into the actual world
Additionally Learn: What’s Mannequin Collapse? Examples, Causes and Fixes
Conclusion
AI environments aren’t background surroundings, they’re the muse of clever behaviour. Chess thrives in totally observable, deterministic worlds whereas self-driving automobiles battle partially observable, stochastic chaos. These 8 dimensions, observability, determinism, competitors, company, dynamics, continuity, episodes, and data dictate algorithm alternative, coaching technique, and deployment success. As AI powers transportation, healthcare, and finance, brokers completely matched to their environments will dominate, intelligence with out the correct stage stays mere potential.
Regularly Requested Questions
A. An atmosphere is every little thing exterior an AI agent interacts with, senses, and acts upon whereas attempting to attain its objective.
A. Setting sorts decide algorithm alternative, coaching technique, and whether or not an AI system can carry out reliably in real-world circumstances.
A. Components like observability, randomness, and dynamics resolve how a lot info an agent has and the way it plans actions over time.
Login to proceed studying and revel in expert-curated content material.